Left-right asymmetry is required for the habenulae to respond to both visual and olfactory stimuli
- Authors
- Dreosti, E., Vendrell Llopis, N., Carl, M., Yaksi, E., and Wilson, S.W.
- ID
- ZDB-PUB-140415-38
- Date
- 2014
- Source
- Current biology : CB 24(4): 440-445 (Journal)
- Registered Authors
- Carl, Matthias, Wilson, Steve, Yaksi, Emre
- Keywords
- none
- MeSH Terms
-
- Animals
- Body Patterning
- Habenula/physiology*
- Olfactory Bulb/physiology*
- Photic Stimulation
- PubMed
- 24508167 Full text @ Curr. Biol.
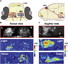
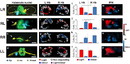
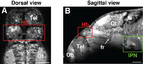
Left-right asymmetries are most likely a universal feature of bilaterian nervous systems and may serve to increase neural capacity by specializing equivalent structures on left and right sides for distinct roles [1]. However, little is known about how asymmetries are encoded within vertebrate neural circuits and how lateralization influences processing of information in the brain. Consequently, it remains unclear the extent to which lateralization of the nervous system is important for normal cognitive and other brain functions and whether defects in lateralization contribute to neurological deficits [2]. Here we show that sensory responses to light and odor are lateralized in larval zebrafish habenulae and that loss of brain asymmetry leads to concomitant loss of responsiveness to either visual or olfactory stimuli. We find that in wild-type zebrafish, most habenular neurons responding to light are present on the left, whereas neurons responding to odor are more frequent on the right. Manipulations that reverse the direction of brain asymmetry reverse the functional properties of habenular neurons, whereas manipulations that generate either double-left- or double-right-sided brains lead to loss of habenular responsiveness to either odor or light, respectively. Our results indicate that loss of brain lateralization has significant consequences upon sensory processing and circuit function.