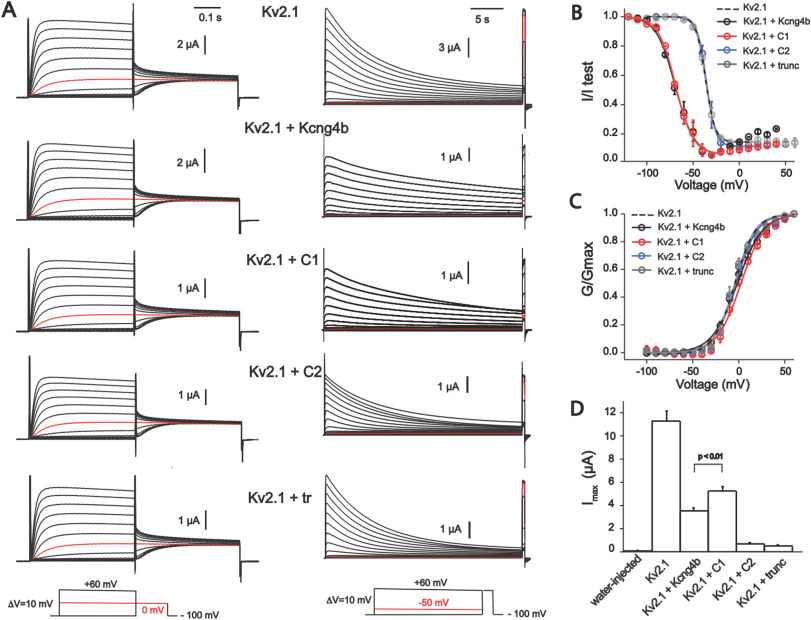
Fig. 4 Biophysical properties of homomeric Kv2.1 (KCNB1) and heteromeric Kv2.1/Kv6.4. (Kcng4b) channels studied in X. laevis oocytes. A - Whole-oocyte current traces of Kv2.1 homomeric and Kv2.1/Kcng4b heteromeric channels elicited by step-depolarization of the oocyte membrane from −100 mV to +60 mV with 10 mV increments (left) for estimation of steady-state activation. Current traces for estimation of the steady-state inactivation of channels is shown to the right. Current was induced by step-depolarization of membrane from −100 mV with 10 mV increments followed by short test pulse to +60 mV for GV curves. The holding potential of oocytes expressing Kv2.1+kcng4b-wt and Kv2.1+kcng4b-C1 was −120 mV in inactivation protocol. The final depolarization step is +40 mV for these channels. Current traces shown in red color correspond to 0 mV for IV protocol and −50 mV for estimation of Steady-state inactivation. B - Steady-state inactivation curves of channels. Solid curves correspond to the fit of the Boltzmann function wit offset to the data points. C - Conduction-voltage (GV) relationship of channels shown in A. Solid curves correspond to the fit of the Boltzmann function to data. D - Current density of channels measured as peak current + 60 mV. Due to very low expression of Kv2.1 + C2 and Kv2.1+ Kcng4b-trunc channels, current traces shown in panel A and data points in B and C correspond to measurements 72–96 h post injection period whereas current amplitudes shown in D reflect 48 h after injection. Error bars in the graphs represent ±SEM. P > 0.01 – Student's unpaired T-test was used to compare the groups; n ≥ 7 for all experiments. Abbreviations: C1 - kcng4b-C1; C2 - kcng4b-C2; Kcng4b-trunc - N-terminal truncated Kcng4b (Shen et al., 2016).
Reprinted from Developmental Biology, 513, Jędrychowska, J., Vardanyan, V., Wieczor, M., Marciniak, A., Czub, J., Amini, R., Jain, R., Shen, H., Choi, H., Kuznicki, J., Korzh, V., Mutant analysis of Kcng4b reveals how the different functional states of the voltage-gated potassium channel regulate ear development, 50-62, Copyright (2024) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Biol.