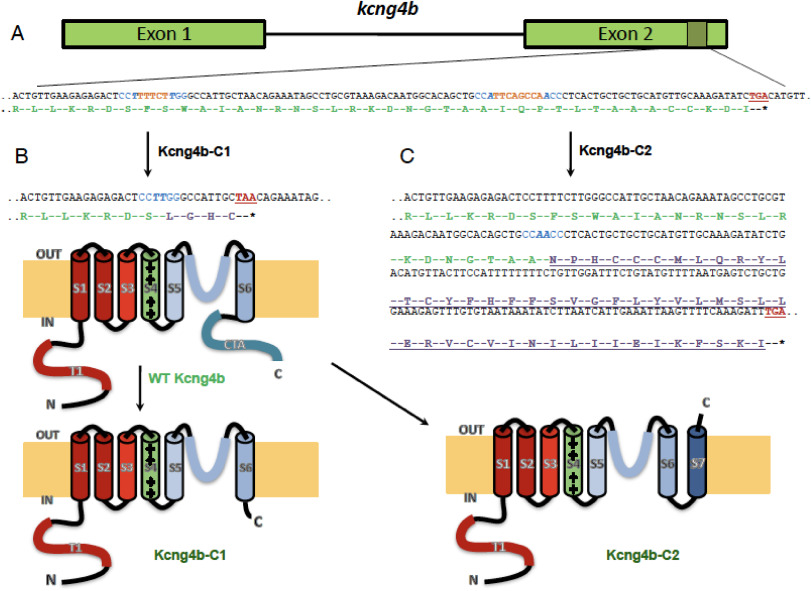
Fig. 1 kcng4b-C1 and kcng4b-C2 mutations differently affect Kcng4b’s C-terminal. A - kcng4b nucleotide sequence is in black, stop-codons are in red, gRNAs' PAM-sequences are in blue, and deleted nucleotides are in orange. The Kcng4b amino-acid sequence is in green, the modified one in lilac. B - mutation kcng4b-C1 caused Kcng4b C-terminal truncation. C - mutation kcng4b-C2 caused an extension of Kcng4b polypeptide and formation of an additional C-terminal TM domain (S7, underlined). T1 and CTA – N- and C-terminal cytoplasmic domains, S1–S7 – TM domains. IN, OUT – intracellular and extracellular space.
Reprinted from Developmental Biology, 513, Jędrychowska, J., Vardanyan, V., Wieczor, M., Marciniak, A., Czub, J., Amini, R., Jain, R., Shen, H., Choi, H., Kuznicki, J., Korzh, V., Mutant analysis of Kcng4b reveals how the different functional states of the voltage-gated potassium channel regulate ear development, 50-62, Copyright (2024) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Biol.