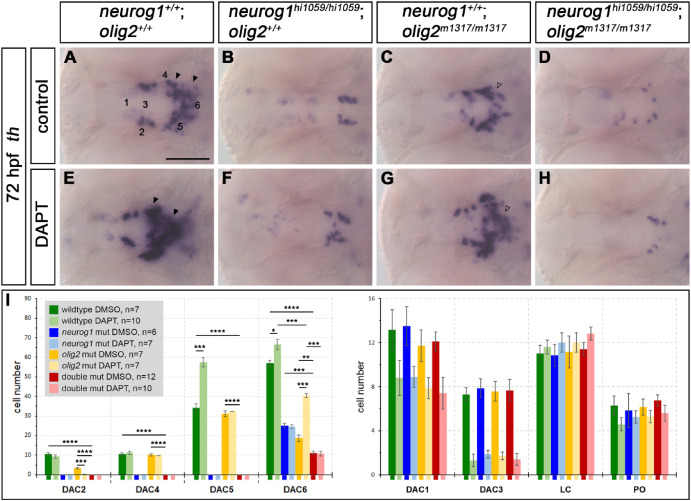
Fig. 2 neurog1 and olig2 single and double mutant phenotypes and Notch inhibition reveal potential epistatic relationships. (A–H) th expression in (A,E) wildtype, (B,F) neurog1hi1059/hi1059 mutants, (C,G) olig2m1317/m1317 mutants and (D,H) neurog1hi1059/hi1059; olig2m1317/m1317 double mutants in (E–H) DAPT treated embryos compared to (A–D) control siblings at 72 hpf. The numbers 1-6 mark the corresponding (DAC1-DAC6) dopaminergic cell clusters (A). The number of th+ DAC5 and DAC6 cells is increased in WT embryos (E) after DAPT treatment, compared to (A) control embryos (filled black arrowheads). The number of th+ DAC6 cells in olig2m1317/m1317 mutant embryos (G) after DAPT treatment is increased compared to control olig2m1317/m1317 mutant embryos (C, open arrowheads). DAPT treatment does not alter the number of th+ cells in neurog1hi1059/hi1059 or double mutant embryos (B,F,D,H). (I) Quantification of th+ cells in single and double mutants compared to wildtype siblings at 72 hpf. The number of embryos analyzed for each genotype are indicated (n-numbers in grey box); p-values were calculated using the Mann-Whitney test. p-values indicate significance if they are <0.05 (*, 0.01–0.05; **, 0.001–0.01; ***, 0.0001–0.001; ****, <0.0001). For numbers see Supplemental Table 2. Abbreviations: numbers 1 through 6 for DAC1-6, dopaminergic cell cluster 1–6; LC, locus coeruleus; PO, preoptic area. All images show single optical planes of dorsal views. Anterior is to the left. Scale bars: 100 μm.
Reprinted from Developmental Biology, 505, Altbürger, C., Rath, M., Armbruster, D., Driever, W., Neurog1 and Olig2 integrate patterning and neurogenesis signals in development of zebrafish dopaminergic and glutamatergic dual transmitter neurons, 859885-98, Copyright (2023) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Biol.