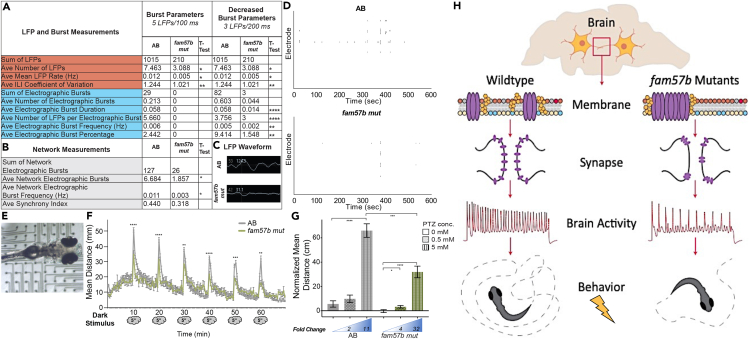
Fig. 8
Decreased spontaneous brain activity and diminished behavioral response after stimuli presentation in fam57b mutants
(A and B) Local field potential (LFP) recordings in unanesthetized live larvae at 7dpf. Brain localized LFP recordings were pooled for each larva. (A) Decreased average number, mean rate and inter-LFP interval (ILI) coefficient of variation of LFP in fam57b mut compared to AB (orange). No electrographic burst activity was identified in fam57b mut at standard 5 LFPs/100 ms. Decreased electrographic burst parameters, including duration, number of LFPs per burst, frequency and percentage at 3 LFPs/200ms (blue). (B) Decreased average electrographic burst network activity and frequency, defined as a minimum or 3 electrographic bursts between 2 electrodes simultaneously, in fam57b mut compared to AB (gray). AB n = 21, fam57b mut n = 24 over 6 experiments. Statistical significance by unpaired ttest, ∗p ≤0.05, ∗∗p ≤ 0.01,∗∗∗p ≤ 0.001,∗∗∗∗p ≤ 0.0001. Technical experimental replicates n = 7.
(C) Representative LFP waveform in brain region, indicating smaller relative waveform in fam57b mut compared to AB.
(D) Representative LFP raster plot over experimental time frame, indicating less overall activity in fam57b mut compared to AB.
(E) Representative image of 7 dpf immersed in cooled agarose in contact with electrodes on 12-well CytoView MEA plate.
(F) Startle response behavioral assay. Light source was removed for 5 s at 10 min intervals. Mean distance reported from tracked movement during 70 min assay. Decreased light startle response identified in fam57b mut compared to AB. Statistical analysis of each startle response by ttest ∗∗p ≤ 0.01, ∗∗∗p ≤ 0.001, ∗∗∗∗p ≤ 0.0001. Error bars SEM. No overall significant change in movement outside of the startle identified. AB n = 125, fam57b mut n = 33 over 5 experiments.
(G) Seizure response behavioral assay. Normalized (baseline recording subtracted) mean distance from tracked movement after absence or presence of pentylenetetrazol (PTZ) 0.5 mM and 5 mM. Significantly increased seizure-induced movement observed at 5mM in AB, while increased movement observed at 0.5 and 5 mM PTZ in fam57b mut. Diminished overall seizure-induced movement at 5 mM in fam57b mut compared to AB. Relative fold change compared to absence of PTZ indicated below histogram. Statistical analysis of each condition by ttest ∗p≤ 0.05, ∗∗∗p ≤ 0.001, ∗∗∗∗p ≤ 0.0001. Error bars SEM. AB n = 166 (0 mM), 92 (0.5 mM), 150 (5 mM), fam57b mut n = 91 (0 mM), 70 (0.5 mM), 56 (5mM) over 6 experiments.
(H) Model proposing role of Fam57b activity in the brain. Loss of function in fam57b mutants indicates significant changes in plasma membrane lipid groups alter architecture of plasma membrane early the developing brain. Architectural changes indicated by increased lipid raft abundance and aggregation. Altered plasma membrane homeostasis results in mis-localization of synaptic proteins, including synaptotagmins, after maturation. Decreased spontaneous brain and network activity suggests diminished synaptic function and developed circuits. As evidence has suggested spontaneous network activity shapes synaptic development, this cycles back to declined neuronal maturation and circuitry. Molecular changes to synaptic function and decreased spontaneous brain activity translate to altered behavioral response after stimuli presentation.