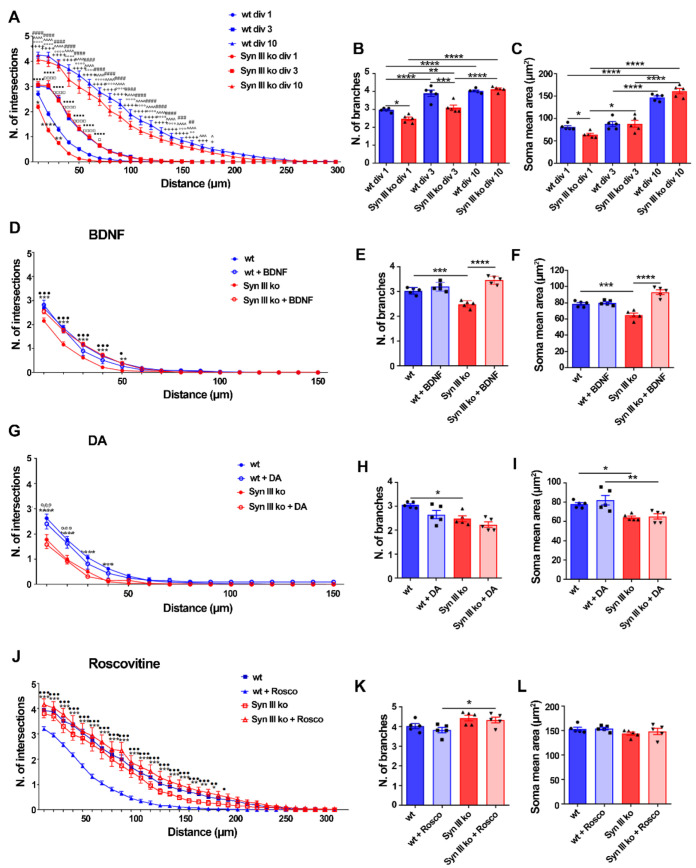
Figure 6
Syn III ko TH-positive mesencephalic neurons exhibit neurodevelopmental deficits involving BDNF and Cdk5 signaling. (A,D,G,J) Sholl analysis assessing the number of intersections. (A) A significant decrease in the number of intersections between the neuronal projections of primary midbrain TH-positive cells and concentric circles in div 1 Syn III ko neurons when compared to wt neurons (**** p < 0.0001, ** p < 0.01, * p < 0.05). A significant increase in the number of intersections was observed in div 10 when compared to div 3 (^ p < 0.05, ^^^ p < 0.001, ^^^^ p < 0.0001) or div 1 wt neurons (+ p < 0.05, +++ p < 0.001, ++++ p < 0.0001) as well as in div 10 to when compared to div 3 (## p < 0.01, ### p < 0.001, #### p < 0.0001) or div 1 Syn III ko neurons (°° p < 0.01, °°° p < 0.001, °°°° p < 0.0001). In Syn III ko neurons a significant increase in the number of intersections at div 3 when compared to div 1 neurons was also detected (■■■■ p < 0.0001, □ p < 0.05, □□□□ p < 0.0001, in wt neurons). (D) Sholl analysis showed that BDNF treatment restored the reduction in the number of intersections in Syn III ko but not in the wt TH-positive cells (*** p < 0.001, ** p < 0.01, Syn III ko vs. wt untreated neurons and ••• p < 0.001, • p < 0.05, untreated vs. treated Syn III ko neurons. (G) DA treatment was not effective in improving the number of intersections in Syn III ko TH-positive cells (*** p < 0.001 and **** p < 0.0001 vs. wt untreated neurons and °°° p < 0.001, vs. wt neurons. (J) Roscovitine treatment reduced number of intersections of wt TH-positive cells, but not that of Syn III ko neurons (*** p < 0.001, ** p < 0.01, * p < 0.05, untreated vs. treated wt neurons and ••• p < 0.001, •• p < 0.01, • p < 0.05, wt vs. Syn III ko neurons. Two-way ANOVA + Bonferroni’s post-test). n = 5 means that plotted values are the mean values deriving from five experiments analyzing 30 TH-positive cells from primary midbrain neuronal cells cultures of either Syn III ko or wt mice. (B,C) TH-positive-neurons from Syn III ko showed a significant reduction in the number of branches stemming from the primary midbrain neuronal cell bodies at div1 (* p < 0.05) and div 3 (*** p < 0.001) when compared to wt mice. A significant decrease of the mean soma area of TH-positive primary midbrain neurons in div 1 Syn III ko when compared to wt cells was detected (* p < 0.05). One-way ANOVA + Newman-Keuls multiple comparison test). n = 5 means that plotted values are the mean values deriving from five experiments analyzing 30 TH-positive cells from primary midbrain neuronal cultures of Syn III ko or wt mice (**** p < 0.0001, ** p < 0.01). (E,F) BDNF treatment also recovered the reduction in the number of branches and mean soma area of Syn III ko neurons (*** p < 0.001, Syn III ko vs. wt untreated neurons, **** p < 0.0001, untreated vs. treated Syn III ko neurons. One-way ANOVA + Newman-Keuls post-test n = 5 means that plotted values are the mean values deriving from five experiments analyzing 30 TH-positive cells from primary midbrain neuronal cells cultures of either Syn III ko or wt mice. (H,I) DA treatment did not either improve the branching or mean soma are of the TH-positive midbrain neurons from Syn III ko mice (* p < 0.05, Syn III ko vs. wt untreated neurons, ** p < 0.01, Syn III ko vs. wt DA-treated neurons, one-way ANOVA + Newman-Keuls). (K,L) The treatment of div 3 primary mouse midbrain neurons with Roscovitine for 24 h did not affect the number of branches and the mean soma area of wt and Syn III ko neurons (* p < 0.05). One-way ANOVA + Newman-Keuls multiple comparison test. n = 5 means that plotted values are the mean values deriving from five experiments analyzing 30 TH-positive cells from primary midbrain neuronal cultures of Syn III ko or wt mice.