Fig. 1
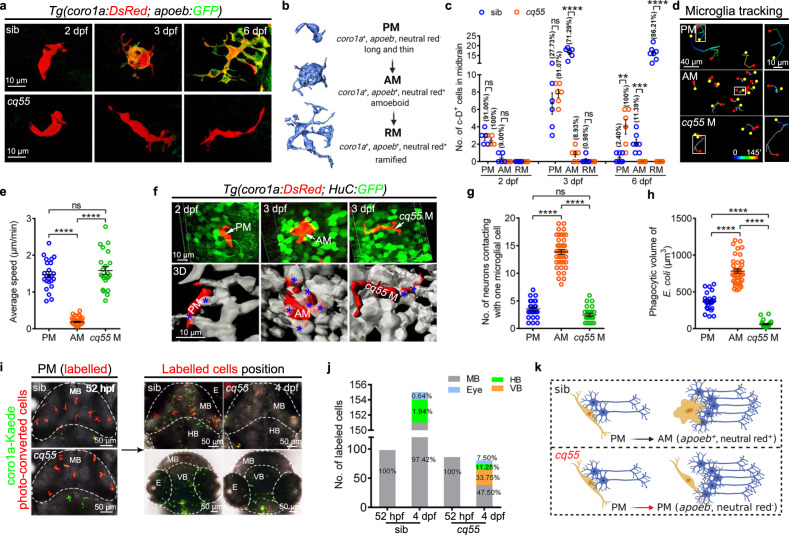
a Representative images of midbrain microglial cells. b Zebrafish microglial development process. c The number and proportion of PM, AM and RM in midbrains (2 dpf: sib and cq55: n = 5; 3 dpf: sib and cq55: n = 6; 6 dpf: sib: n = 7, cq55: n = 6). Each dot denotes one fish. d The movement trajectory of c-D+ cells during 145 min. Each line represents one cell. The right panels are the enlarged images of boxed cells. The yellow circle and red square indicates start and end points, respectively. e The movement speed of c-D+ cells in d (n = 23 PM, 41 AM and 22 cq55 M from 6 fish per group). f Representative images (top) and 3D reconstructions (bottom) of c-D+ PM, AM or cq55 M (red) contacting HuC-GFP+ neurons (green and white colors in top and bottom panels). White arrows and blue asterisks mark the c-D+ cells and touched neurons. g The numbers of H-G+ neurons contacting PM, AM or cq55 M (n = 24 PM from 6 fish; n = 40 AM from 5 fish; n = 24 cq55 M from 6 fish). h The volume of phagocytized E. coli (n = 23 PM from 6 fish; n = 40 AM from 5 fish; n = 23 cq55 M from 6 fish). i Imagings of c-K+ PM (left panel). Coronal (right top) and transverse (right bottom) views of red c-K+ cells at 4 dpf. j The number and proportion of red c-K+ cells in different regions in (i) (n = 10 per group). k Schematic overview of microglia phenotypes, created with BioRender.com. sib siblings, M microglia, PM pre-microglia, AM amoeboid microglia, RM ramified microglia, c-D coro1a-DsRed, c-K coro1a-Kaede, MB midbrain, HB hindbrain, VB ventral brain, E eye. The numbers (c) and (j) indicate the average percentage. Each dot in (e), (g), and (h) represents one cell. Error bars, mean ± SEM. **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001; ****P < 0.0001; ns no significant, Unpaired two-tailed Student’s t test. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.