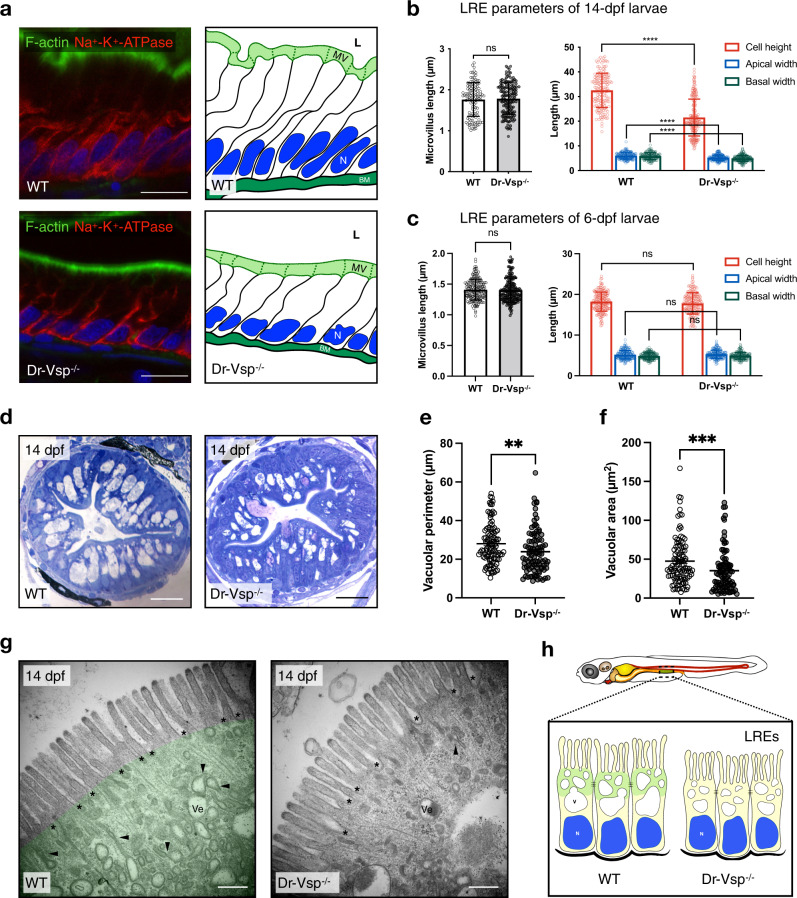
Fig. 7
a Immunostaining showing cellular framework in sagittal sections of 14-dpf wild-type (WT) and Dr-Vsp−/− LREs; and their corresponding schematic illustration. Green, F-actin. Red, Na+-K+ ATPase. Blue, DAPI. Scale bar = 10 µm. b Cellular parameters of LREs at 14 dpf comparing wild-type and Dr-Vsp−/− zebrafish larvae. (Left) Microvillus length. (Right) Cell height, apical width, and basal width. Enterocytes, ≥120 cells from five larvae for each zebrafish line. c Cellular parameters of LREs at 6 dpf comparing wild-type and Dr-Vsp−/− zebrafish larvae. (Left) Microvillus length. (Right) Cell height, apical width, and basal width. Enterocytes, ≥170 cells from six larvae for each zebrafish line. Error bars, means ± SD; ****P < 0.0001; unpaired Student’s t-test; ns no statistically significant difference. d Representative transverse sections at mid-intestine of 14-dpf wild-type and Dr-Vsp−/− zebrafish larvae, showing LREs with intracellular supranuclear vacuoles. Sections were stained with toluidine blue. Scale bar = 20 µm. e, f Vacuole parameters of 14-dpf LREs. e Vacuolar perimeter of wild-type and Dr-Vsp−/− LREs. **P = 0.0024; Mann–Whitney U-test. Vacuoles, 108 for wild-type and 95 for Dr-Vsp−/−. Data were collected from three larvae for each zebrafish line. f Vacuolar area of wild-type and Dr-Vsp−/− LREs from the same samples as in Fig. 6e. ***P = 0.0003; Mann–Whitney U-test. g Representative TEM images at mid-intestine of 14-dpf wild-type and Dr-Vsp−/− zebrafish LREs, showing the ultrastructures of microvilli and subapical region. Key features of absorptive enterocytes are presented, including membrane invaginations at inter-microvillous spaces (*), cytoplasmic tubules and tubule-vacuole complexes (arrowhead), and numerous endocytic vesicles (Ve). In wild-type LRE, green represents the region upper to the supranuclear vacuole, which corresponds to the area with a positive immunofluorescence signal of Dr-Vsp in Fig. 3a, b. Scale bar = 500 nm. h Schematic diagram of wild-type and Dr-Vsp−/− LREs. Dr-Vsp (green) is primarily localized in the cytoplasm close to the apical surface of enterocytes, promoting endosomal maturation during endocytosis-dependent nutrient absorption. N nucleus, V vacuoles.