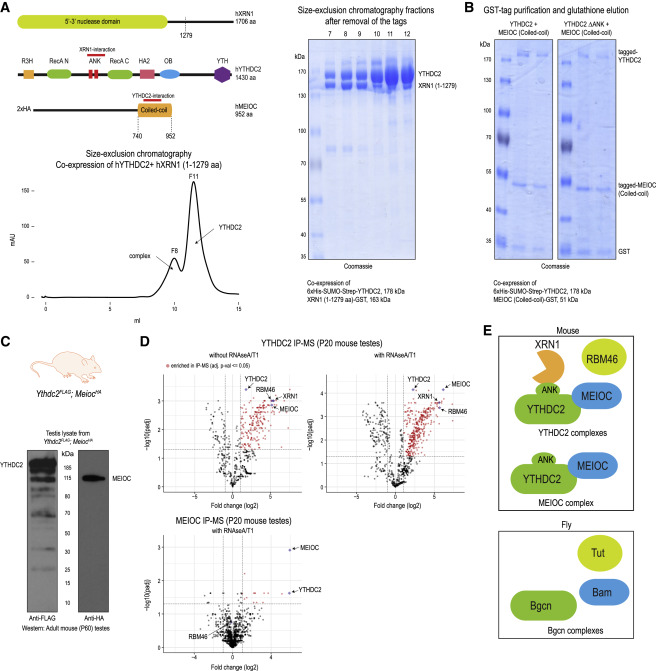
Fig. 2 Figure 2. YTHDC2 directly interacts with XRN1 and MEIOC, and associates with RBM46 (A) Cartoon showing domain organization of human YTHDC2, XRN1 and MEIOC. The interaction regions in the proteins are marked. Size-exclusion chromatography protein elution trace showing the presence of YTHDC2-XRN1(1-1279 aa) complex and free YTHDC2 protein. Indicated fractions were analyzed by SDS-PAGE to reveal presence of YTHDC2- XRN1(1-1279 aa) complex (fractions 7-9) and free YTHDC2 (fractions 10–12). See also Figure S2A. (B) Co-expression YTHDC2 and MEIOC-coiled-coil (CC) domain in insect cells as tagged proteins, followed by purification over glutathione-Sepharose beads to isolate MEIOC-CC. SDS-PAGE analysis shows the co-purification of YTHDC2 with MEIOC-CC (left panel). Deletion of the ANK repeats of YTHDC2 does not affect this association (right panel). (C) Western blot of testicular lysate showing expression of YTHDC2-3xFLAG and 2xHA-MEIOC from double-knockin Ythdc2FLAG;MeiocHA mice. (D) Purification of protein complexes using anti-FLAG or anti-HA affinity beads. Complexes were treated with RNases (RNase A/T1), when indicated. Mass spectrometry identification of complex components is shown. The volcano plot shows the enrichment of proteins in purifications from knockin mouse testes lysates compared to that from wildtype mouse testes. See also Table S3. (E) Cartoon showing the different protein associations of mouse YTHDC2 as established in this study in mouse testes. Complex components previously reported to be associating with YTHDC2 fly ortholog Bgcn is also shown.
Image
Figure Caption
Acknowledgments
This image is the copyrighted work of the attributed author or publisher, and
ZFIN has permission only to display this image to its users.
Additional permissions should be obtained from the applicable author or publisher of the image.
Full text @ Mol. Cell