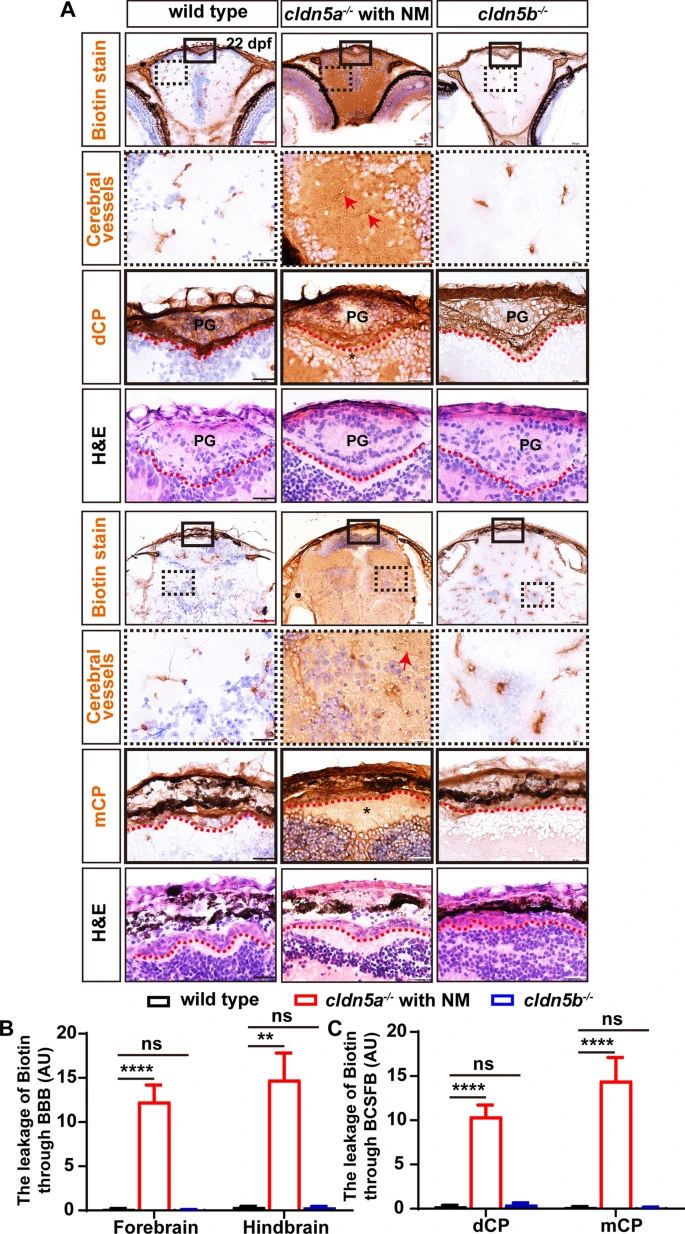
Fig. 4
The leakage of sulfo-NHS-biotin through BBB and BCSFB in cldn5a-/-. A Sulfo-NHS-biotin (443 Da) was injected into the circulation system to assess the tightness of BBB and BCSFB in 22 dpf-old zebrafish larvae. In wild-type biotin signals are distributed in cerebral vessels, pineal gland (PG), and inside the CPs (both dCP and mCP), but not in brain parenchyma and ventricle. In cldn5a-/- with NM, biotin was permeated through the cerebrovasculatures (red arrows) into the whole brain. In the brains of cldn5b-/-, biotin stays in the cerebral vessels, PG, and inside the CPs. Serial sections were stained with HE to show the histology of CPs. Black dashed rectangles and solid rectangles indicate the enlarged regions of cerebral vessels and CPs respectively which are shown in the lower panels with high magnification. Red dot lines describe the linear CP epithelial cells. Black asterisks indicated the brain ventricles beneath the CPs with leaky biotin. Scale bars: 100 μm in red and 20 μm in black. B Quantification of the biotin signal strength of the biotin leaks through BBB into brain parenchyma. C Quantification of the signal strength of the leaked biotin through BCSFB. n > 3 fishes analyzed per group. Data are represented as mean ± SEM; **P < 0.01, ****P < 0.001. ns means no significance