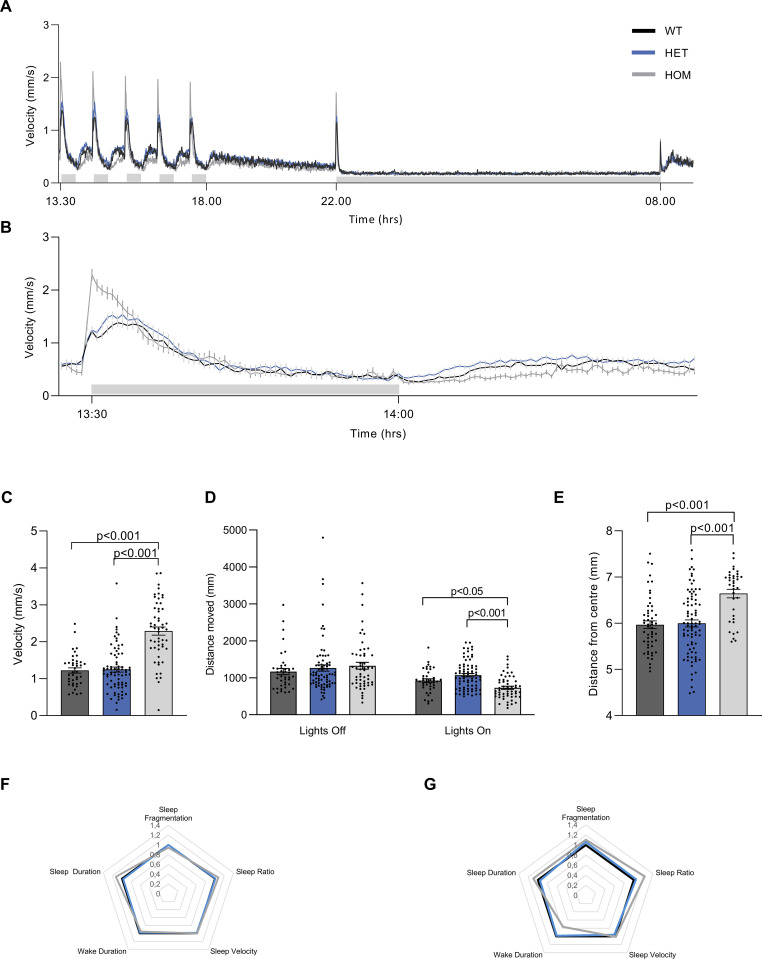
Fig 1
(A) Swim velocity of homozygous wild type (WT, n = 40), heterozygous vmat2 (HET, n = 76) and homozygous vmat2 (HOM, n = 53) larvae depicting the 30-minute intervals of lights-off (grey shaded bar) and lights-on phases between 13:30 and 18:00, followed by constant light-on from 18:00 to 22:00. Lights were turned off for the night (grey shaded bar) from 22:00 to 8:00 the next morning when the lights were turned on again. (B) Swim velocity of homozygous wild type (n = 40), heterozygous vmat2 (n = 76) and homozygous vmat2 (n = 53) larvae during the first hour of lights-off (grey shaded bar) and lights-on. (C) At the onset of the first lights-off phase, peak velocity was analysed and it was revealed that homozygous vmat2 larvae exhibited a higher peak velocity than wild type and heterozygous larvae. (D) The total distance moved during the first 30-minutes of lights-off and the following 30-minutes of lights-on demonstrates that homozygous vmat2 larvae moved significantly less during lights-on than wild type or heterozygous larvae, while there was no difference during lights-off between all three strains. (E) Thigmotaxis was evaluated for wild type (n = 53), heterozygous vmat2 (n = 83) and homozygous vmat2 (n = 36) larvae as the distance of the larvae from the well centre during lights-on between 18:00 and 22:00. Homozygous vmat2 larvae tended to dwell closer to the edge of the well than heterozygous and wild type larvae. (F) Sleep parameters in wild type, heterozygous vmat2 and homozygous vmat2 larvae were examined during the night, 10-hour lights-off phase. No significant differences between genotypes were observed in any of the sleep parameters. (G) Sleep parameters in wild type, heterozygous vmat2 and homozygous vmat2 larvae were examined during a 30-minute lights-on segment following the 10-hour lights-off, homozygous vmat2 larvae exhibited significantly higher sleep ratio during this time. Sleep parameter data are represented as fold change of wild type larvae.