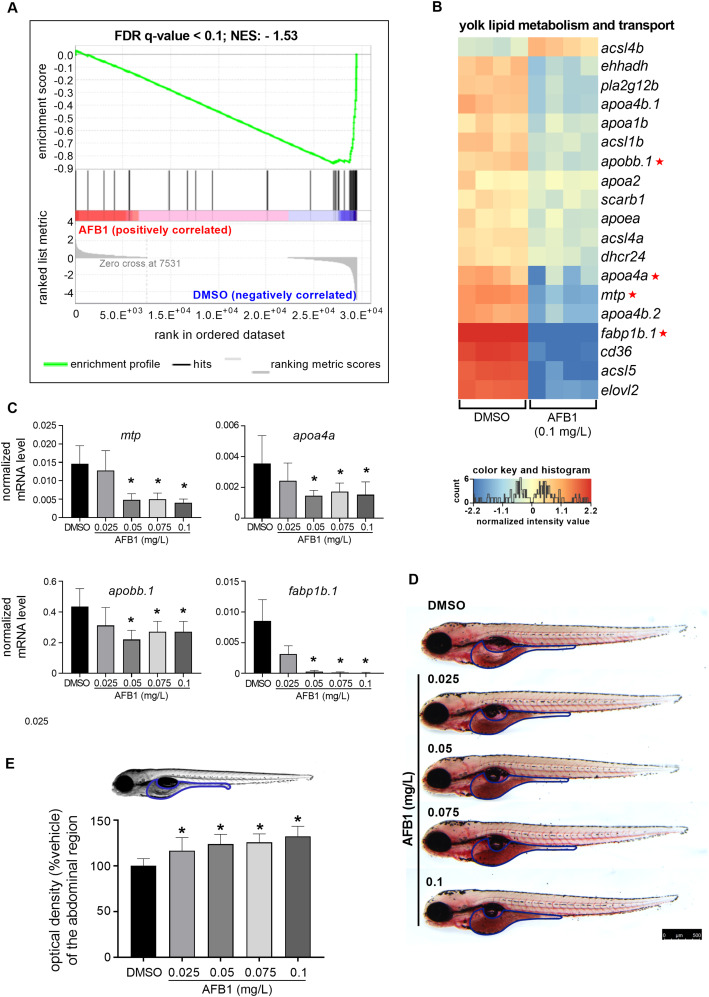
Fig. 7 Embryonic exposure to AFB1 disrupts yolk lipid metabolism in zebrafish larvae. (A) Gene set enrichment analysis (GSEA) of lipid metabolism and transport-associated genes in 120 hpf zebrafish larvae exposed to 0.1 mg/L AFB1. The selected lipid-associated genes were identified in the zebrafish yolk by Fraher et al. (2016). FDR: false discovery rate; NES: normalized enrichment score. (B) Heat map illustrating the expression level of 19 lipid-associated genes identified by GSEA between the control and the AFB1-exposed larvae. Data represent the normalized gene expression values of the four independent biological replicates per treatment. Red asterisks indicate the selected genes for RT-qPCR. (C) RT-qPCR-based analysis of four selected yolk lipid metabolism and transport-related genes after embryonic exposure to different sub-lethal concentrations of AFB1 (n = 5 replicates, n = 30 pooled larvae per replicate) (D) Representative images of Oil Red O (ORO) stained 120 hpf larvae after AFB1 exposure. ORO staining indicates the lipid content and distribution in the larvae. Scale bar = 500 µm. (E) Lipid content was evaluated by optical density (OD) measurement. The graph showing OD values of the abdominal region relative to the control (100%) after AFB1 exposure (n = 2 replicates, n = 10 larvae per replicate). Data represent the mean and SD. “*” indicates statistical significance at p < 0.05 vs. the control (DMSO).
Reprinted from Journal of hazardous materials, 416, Ivanovics, B., Gazsi, G., Reining, M., Berta, I., Poliska, S., Toth, M., Domokos, A., Nagy, B., Staszny, A., Cserhati, M., Csosz, E., Bacsi, A., Csenki-Bakos, Z., Acs, A., Urbanyi, B., Czimmerer, Z., Embryonic exposure to low concentrations of aflatoxin B1 triggers global transcriptomic changes, defective yolk lipid mobilization, abnormal gastrointestinal tract development and inflammation in zebrafish, 125788, Copyright (2021) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ J. Hazard. Mater.