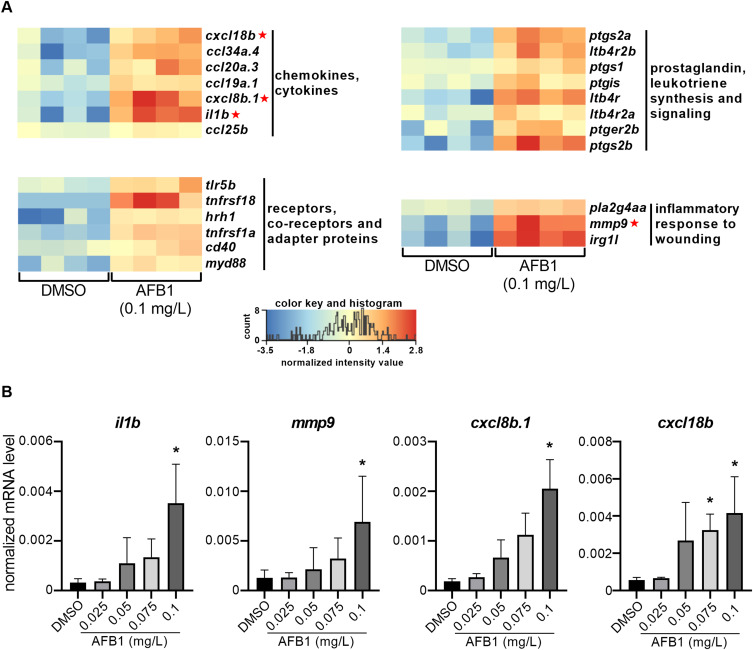
Fig. 3 AFB1 induces the expression of immune- and inflammation-related genes in zebrafish larvae. (A) Heat maps illustrating the significantly up-regulated immune response- and inflammation-associated genes in the AFB1 (0.1 mg/L) -exposed 120 hpf zebrafish larvae compare to the control. Data represent the normalized gene expression values of the four independent biological replicates per treatment. Red asterisks indicate the selected genes for RT-qPCR. (B) RT-qPCR-based gene expression on a set of AFB1-induced inflammatory genes in the AFB1 (0.025–0.1 mg/L) -exposed 120 hpf zebrafish larvae (n = 5 replicates, n = 30 pooled larvae per replicate). Data represent the mean and SD. “*” indicates statistical significance at p < 0.05 vs. the control (DMSO).
Reprinted from Journal of hazardous materials, 416, Ivanovics, B., Gazsi, G., Reining, M., Berta, I., Poliska, S., Toth, M., Domokos, A., Nagy, B., Staszny, A., Cserhati, M., Csosz, E., Bacsi, A., Csenki-Bakos, Z., Acs, A., Urbanyi, B., Czimmerer, Z., Embryonic exposure to low concentrations of aflatoxin B1 triggers global transcriptomic changes, defective yolk lipid mobilization, abnormal gastrointestinal tract development and inflammation in zebrafish, 125788, Copyright (2021) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ J. Hazard. Mater.