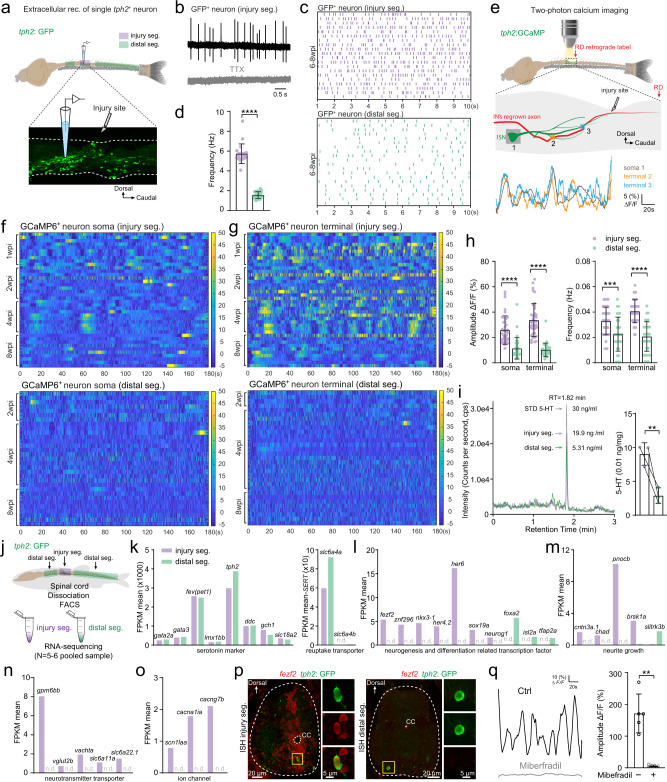
Fig. 3
a Illustration of the in vitro spinal cord preparation for extracellular recording of the single GFP+ ISN in the injury segment (purple) and distal segments (green). b Representative extracellular recording trace of a single injury-induced GFP+ ISN spontaneous firing in the absence (upper) or presence (lower) of 1 µM TTX. c, d Raster plots (c) and quantification (d) of the spontaneous firing frequency of GFP+ ISNs in the injury segment and distal segments within 10 s. e Two-photon calcium imaging is used to examine the Ca2+ homeostasis (top) in in vitro spinal cord preparation. Typical examples of Ca2+ changes (bottom) are recorded in the GCaMP6+ ISN soma (gray) and two terminal varicosities (orange and blue) around the interneuron’s regrown axon at the injury site (middle). f, g Heatmaps showing Ca2+ oscillations during 3 min of GCaMP6+ ISNs soma in the injury segment (f upper) and distal segments (f lower), and GCaMP6+ ISNs terminal in the injury segment (g upper) and distal segments (g lower). h Quantification of Ca2+ oscillations amplitude and frequency of GCaMP6+ ISNs soma and terminal in the injury segment and distal segments. i (left) Representative LC–MS chromatograms showing retention time of standard serotonin (gray), extracellular fluid samples from injury segments (purple) and distal segments (green). (right) Quantification of serotonin released extracellularly per unit spinal cord tissue. j Sampling of GFP+ ISNs from the injury segment and distal segments of the same SCI animal for FAC-sorting and bulk RNA-seq. k–o Mean FPKM values of common serotonin markers and reuptake transporter genes (k); differentially expressed (P value < 0.05) neurogenesis and neuron differentiation related transcription factors (l); neurite growth related genes (m); neurotransmitter transporter related genes (n); ion channel genes including calcium channel gene cacna1ia (voltage-dependent t-type calcium channel) (o) in GFP+ ISNs from the injury segment and distal segments. n.d. denotes not detected. p In situ hybridization (ISH) for fezf2 combining staining for GFP on cross sections of the injury and distal spinal segment, representing results from three independent experiments. Expanded images indicated by yellow boxes showing co-labeled cells. q Representative traces and mean amplitude of the robust Ca2+ activity in GCaMP6+ ISNs terminal in the injury segment in the absence (black) and presence (gray) of Calcium channel blocker miberfradil (3 µM). All data are presented as mean ± SD. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001, significant difference. For detailed statistics, see Supplementary Table 1.