Figure 2
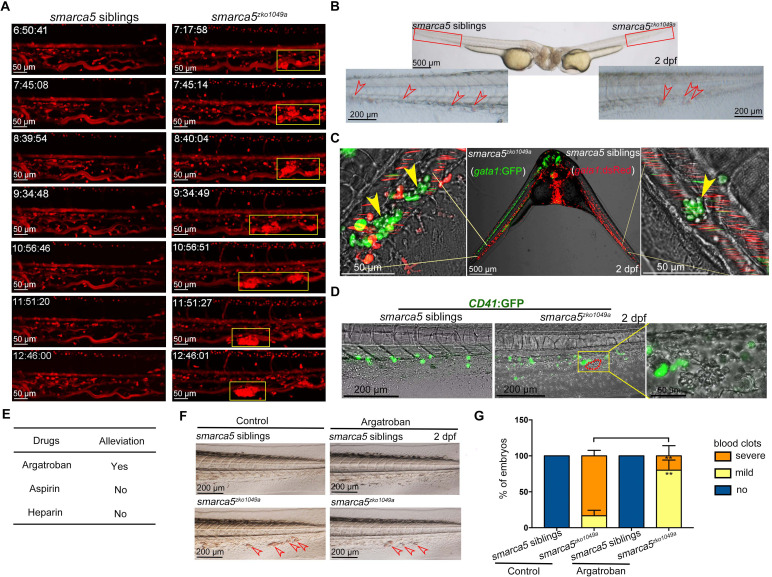
(A) The snapshot of Tg (gata1:dsRed) in smarca5zko1049a and their siblings from 36 hpf to 2 dpf. The yellow rectangular boxes in CHT show the formed blood clots smarca5zko1049a. (B) The bright-field of parabiosis at 2 dpf between smarca5zko1049a and their siblings. The amplification region in the red rectangular box in CHT shows the blood clots (indicated by arrow heads) in smarca5zko1049a and their siblings. (C) The confocal imaging of parabiosis generated between smarca5zko1049a and their siblings with Tg (gata1:GFP) and Tg (gata1:dsRed) background, respectively. The magnification in CHT shows the aggregation of gata1:GFP+ cells (indicated by arrow heads) in the caudal vein plexus. (D) The confocal imaging of Tg (CD41:GFP) in smarca5zko1049a and their siblings at 2 dpf. The magnification in the yellow rectangular box in CHT shows the blood clots and the distribution of CD41:GFP+ cells. (E) Drugs used to examine whether the blood clots in smarca5zko1049a can be alleviated. (F) The bright-field of tail region in smarca5zko1049a at 2 dpf in control group and with argatroban treatment. The blood clots are indicated by arrow heads. (G) The quantification of blood clots phenotype in (F). Data are mean ± s.d. (G). Asterisk presents statistical significance (**p< 0.01). p Values were calculated by two-tailed unpaired Student’s t-test.
The blood clots are formed by RBC aggregation.
Image
Figure Caption
Figure Data
Acknowledgments
This image is the copyrighted work of the attributed author or publisher, and
ZFIN has permission only to display this image to its users.
Additional permissions should be obtained from the applicable author or publisher of the image.
Full text @ Elife