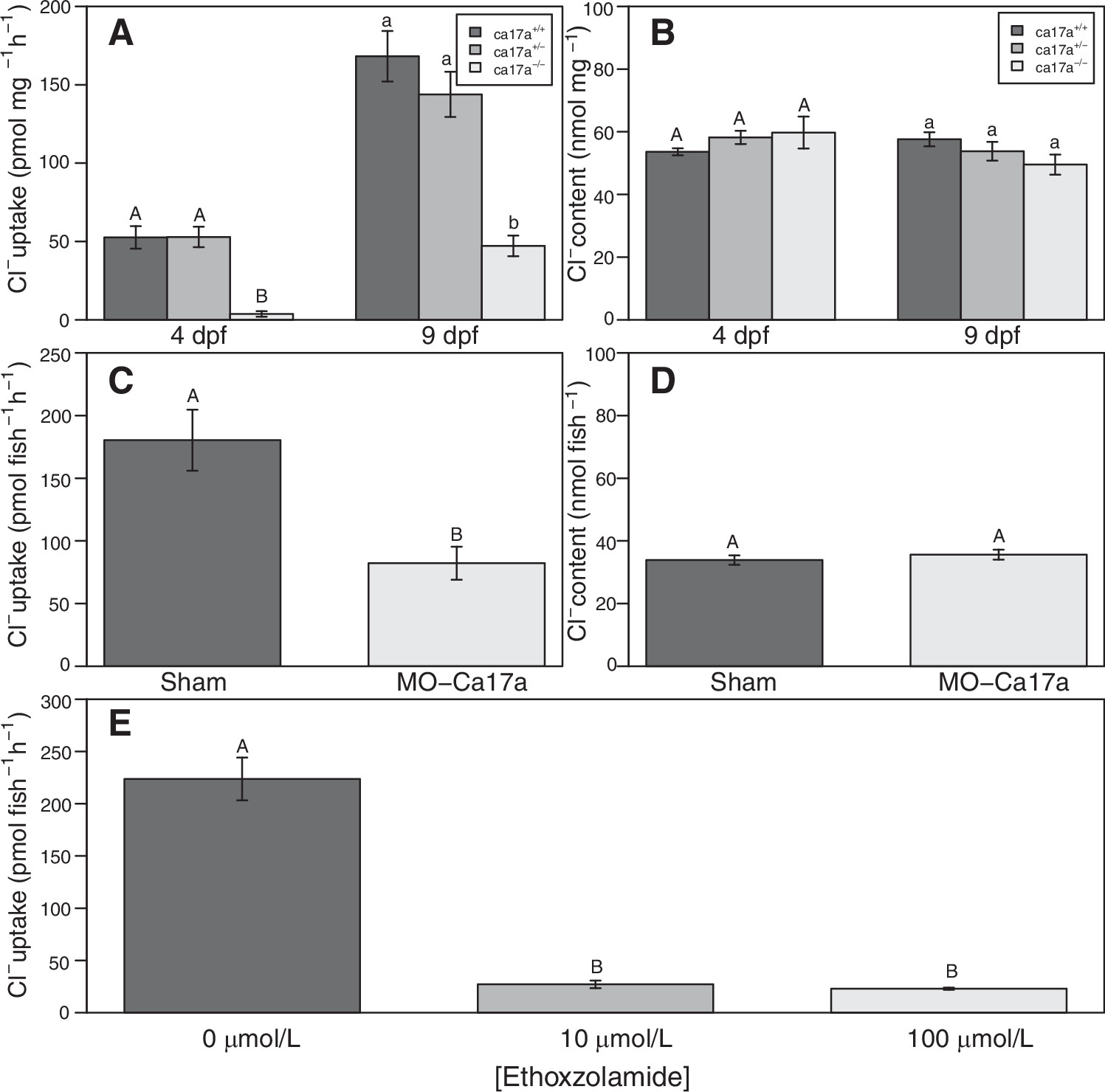
Fig. 4 Cl− uptake rates and whole body Cl− content of ca17a+/+, ca17a+/−, and ca17a−/− larvae (A and B), as well as sham Ca17a morpholino-treated larvae (C and D), and the effect of ethoxzolamide on Cl− uptake (E) in zebrafish (Danio rerio) larvae. There was a significant effect of genotype on Cl− uptake in 4- and 9-dpf larvae (A) (ANOVA; 4 dpf: F = 55.1, P < 0.01, n = 16 for ca17a+/+ and ca17a+/−, n = 12 for ca17a−/−; 9 dpf: F = 21.5, P < 0.01, n = 13 for ca17a+/+, n = 12 for ca17a+/−, n = 11 for ca17a−/−) but not Cl− content in 4 dpf (B) (ANOVA; F = 1.1, P = 0.36, n = 7 for ca17a+/+ and ca17a+/−, n = 6 for ca17a−/−) or 9 dpf (ANOVA; F = 1.9, P = 0.18, n = 8 for ca17a+/+ and ca17a+/−, n = 5 for ca17a−/−) larvae. There was an effect of Ca17a knockdown on Cl− uptake in 4-dpf zebrafish (C) (Welch’s two-sample t test; t = 3.5, P < 0.01, n = 6), but not Cl− content (D) (Welch’s two-sample t test; t = −0.8, P = 0.5, n = 6). There was an effect of ethoxzolamide on Cl− uptake in 4-dpf zebrafish (E) [one-way nonparametric ANOVA (Kruskal–Wallis); χ2 = 12.1, P < 0.01, n = 6]. Values with different letters are significantly different (P < 0.05) from one another. Data are presented as means ± SE. dpf, days postfertilization.
Image
Figure Caption
Figure Data
Acknowledgments
This image is the copyrighted work of the attributed author or publisher, and
ZFIN has permission only to display this image to its users.
Additional permissions should be obtained from the applicable author or publisher of the image.
Full text @ Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol.