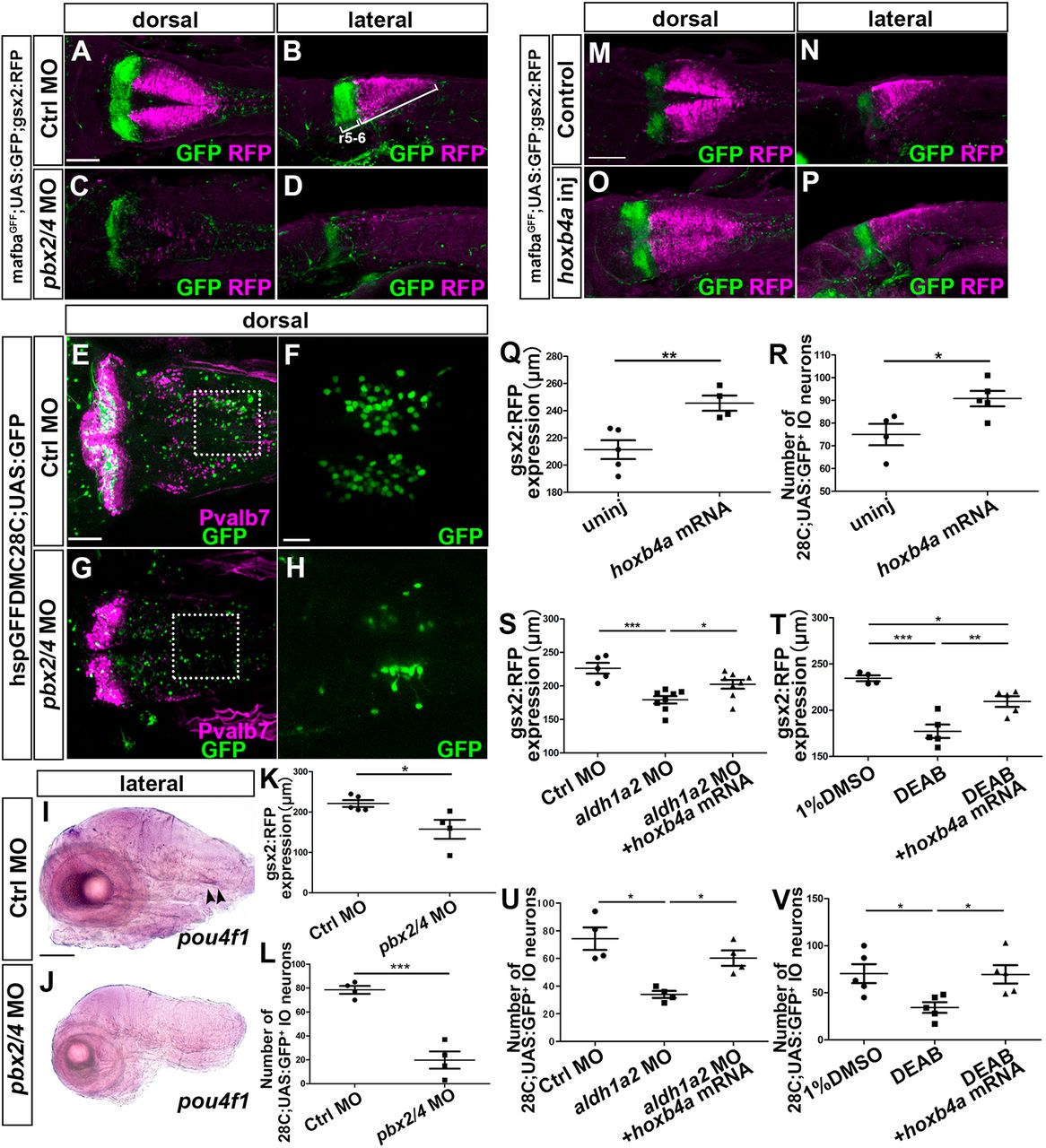
Fig. 10 Hox genes are involved in gsx2 expression and IO neuronal development. (A-D) 3 dpf control morphant (A,B, n=5) and pbx2/4 morphant (C,D, n=4) mafbaGFF;UAS;GFP;gsx2:RFP larvae were stained using anti-RFP (magenta) and anti-GFP (green) antibodies. (E-H) 5 dpf control morphant (E,F, n=4) and pbx2/4 morphant (G,H, n=4) 28C;UAS:GFP larvae stained using anti-Pvalb7 (magenta) and anti-GFP (green) antibodies. (I,J) Expression of pou4f1 in 5 dpf control morphant (I) and pbx2/4 morphant (J) larvae. The pou4f1 signal is marked by arrowheads. (K,L) Length of the gsx2:RFP+ hindbrain region (K) and number of 28C;UAS:GFP+ IO neurons (L) in control and pbx2/4 morphant larvae. (M-P) 3 dpf control (M,N, n=4) and 25 pg hoxb4a RNA-injected (O,P, n=4) larvae were stained with anti-RFP (magenta) and anti-GFP (green) antibodies. (Q,R) Length of the gsx2:RFP+ hindbrain region (Q) and number of 28C;UAS:GFP+ neurons (R) in control and hoxb4a RNA-injected larvae. (S,T) Length of the gsx2:RFP+ hindbrain region in control (n=5), aldh1a2 morphant (n=8) and hoxb4a RNA-injected aldh1a2 morphant larvae (n=8) (S); in control (1% DMSO-treated, n=4), DEAB-treated (n=5), hoxb4a RNA-injected and DEAB-treated larvae (n=5) (T). (U,V) Number of 28C;UAS:GFP+ neurons in control (n=4), aldh1a2 morphant (n=4), and hoxb4a RNA-injected aldh1a2 morphant larvae (n=4) (U); in control (1% DMSO-treated, n=5), DEAB-treated (n=5), hoxb4a RNA-injected and DEAB-treated larvae (n=5) (V). *P<0.05; **P<0.01; ***P<0.001 (Student's t-test for K,L,Q,R, and one-way ANOVA with Tukey's multiple comparison test for S-V). Data are mean±s.e.m. with individual values indicated. Scale bars: 100 µm in A (applies to A-D), M (applies to M-P) and I (applies to I,J); 50 µm in E (applies to E,G); 20 μm in F (applies to F,H).
Image
Figure Caption
Figure Data
Acknowledgments
This image is the copyrighted work of the attributed author or publisher, and
ZFIN has permission only to display this image to its users.
Additional permissions should be obtained from the applicable author or publisher of the image.
Full text @ Development