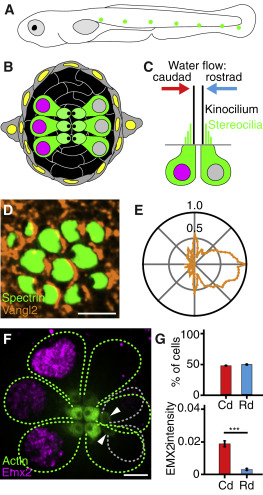
Fig. 1 Organization of Neuromasts in the Zebrafish’s Lateral Line (A) A schematic drawing of a 4 dpf larva depicts neuromasts (green) of the posterior lateral line. Additional, unshown neuromasts adorn the anterior portion of the larva. (B) A diagrammatic surface view of a single neuromast shows hair cells (green) separated by supporting cells (black) and surrounded by mantle cells (gray). (C) A schematic section depicts the sensitivity of oppositely oriented hair cells to water flow. (D) In a micrograph of the upper surface of a neuromast, spectrin (green) marks the cuticular plates of hair cells. Immunolabeling reveals that the core PCP protein Vangl2 (orange) occurs consistently at the posterior cellular boundaries. (E) A polar plot of average Vangl2 labeling from 502 hair cells quantitates the effect in (D). This and each of the subsequent polar plots represents the average intensity of labeling, normalized to the maximum value, as a function of angular position with respect to the cells’ centers. (F) In a developing neuromast, Emx2 (magenta) is expressed in the nuclei of three mature hair cells (green dashed lines on the left). In the distribution of actin-GFP (green) at the cellular apices, the dark spots locate the kinocilia and indicate that those cells are sensitive to caudad stimulation. Three other mature hair cells (green dashed lines on the right) have an opposite orientation. The apices of two immature hair cells (gray dashed lines) are indicated by arrowheads. (G) The polarities of hair cells from 20 neuromasts (top) in 4 dpf larvae are equally divided between caudad (Cd; 135 cells) and rostrad (Rd; 141 cells). The former cells express significantly higher levels of Emx2 (bottom). Scale bars, 3 μm. Means ± SEM; ∗∗∗p < 0.001. See also Figure S1.
Image
Figure Caption
Figure Data
Acknowledgments
This image is the copyrighted work of the attributed author or publisher, and
ZFIN has permission only to display this image to its users.
Additional permissions should be obtained from the applicable author or publisher of the image.
Full text @ Curr. Biol.