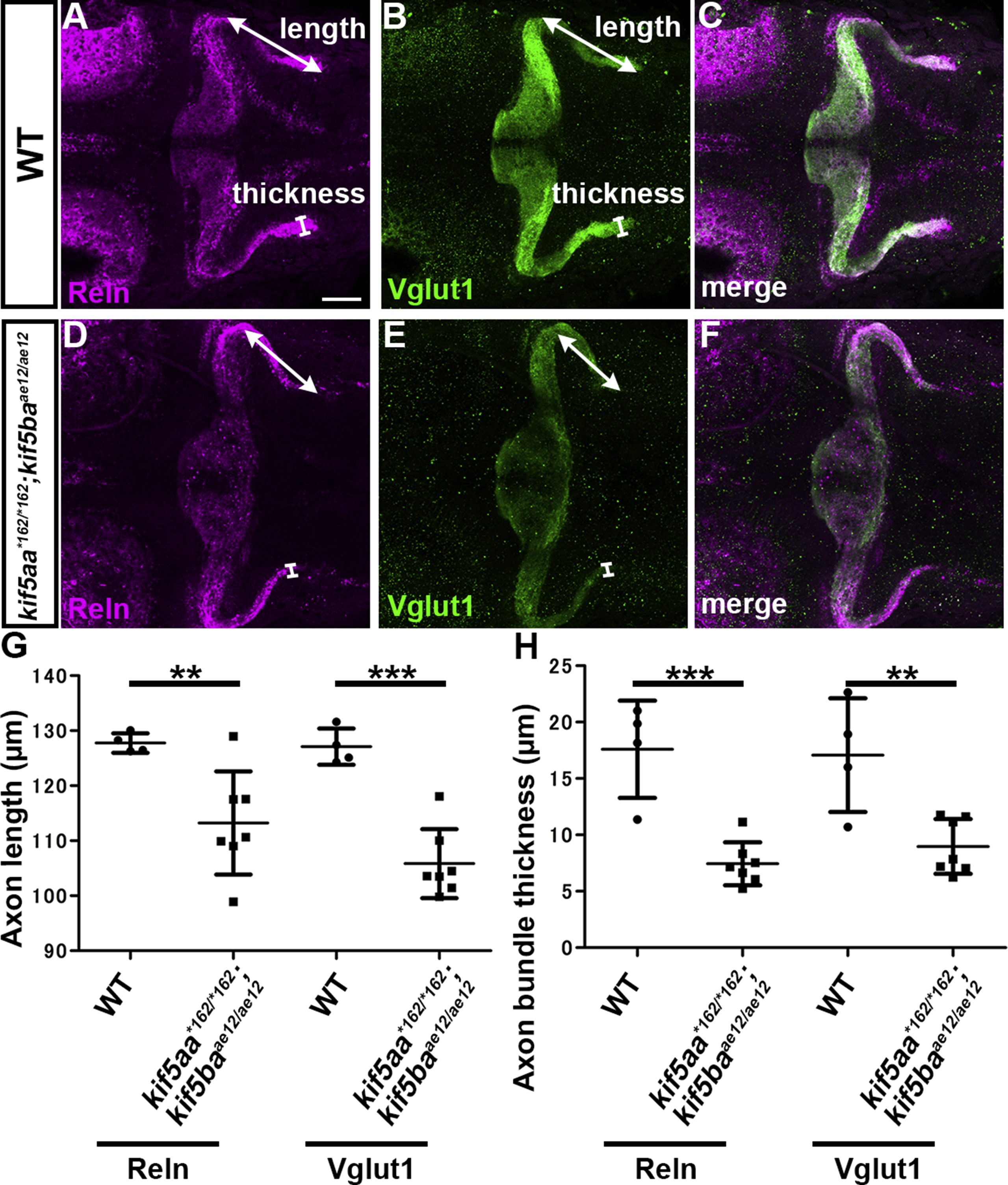
Fig. S16
Kinesin-dependent localization of Reln protein. (A-F) Reln protein and granule cell (GC) axons. 5-dpf WT (A-C, n= 4) and kif5aa*162/*162; kif5baae12/ae12 double mutant (D-F, n= 7) larvae were stained with anti-Reln (magenta) and anti-Vglut1 (green) antibodies. Dorsal views with anterior to the left. Scale bars: 50 μm in A (applies to A-F). (G) The length and thickness of the Reln+ and Vglut1+ extra-cerebellar domains were measured and plotted. Both the length and the thickness of the Reln+ and Vglut1+ domains were significantly different in kif5aa; kif5bamutants compared to WT (**p < 0.01; ***p< 0.001; Welch’s t-test for Reelin and Student’s t-test for Vglut1). Note that the granule cell axons were shorter, and Reln protein did not diffuse beyond the axons in the kif5aa; kif5ba mutant hindbrain.
Reprinted from Developmental Biology, 455(2), Nimura, T., Itoh, T., Hagio, H., Hayashi, T., Di Donato, V., Takeuchi, M., Itoh, T., Inoguchi, F., Sato, Y., Yamamoto, N., Katsuyama, Y., Del Bene, F., Shimizu, T., Hibi, M., Role of Reelin in cell positioning in the cerebellum and the cerebellum-like structure in zebrafish, 393-408, Copyright (2019) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Biol.