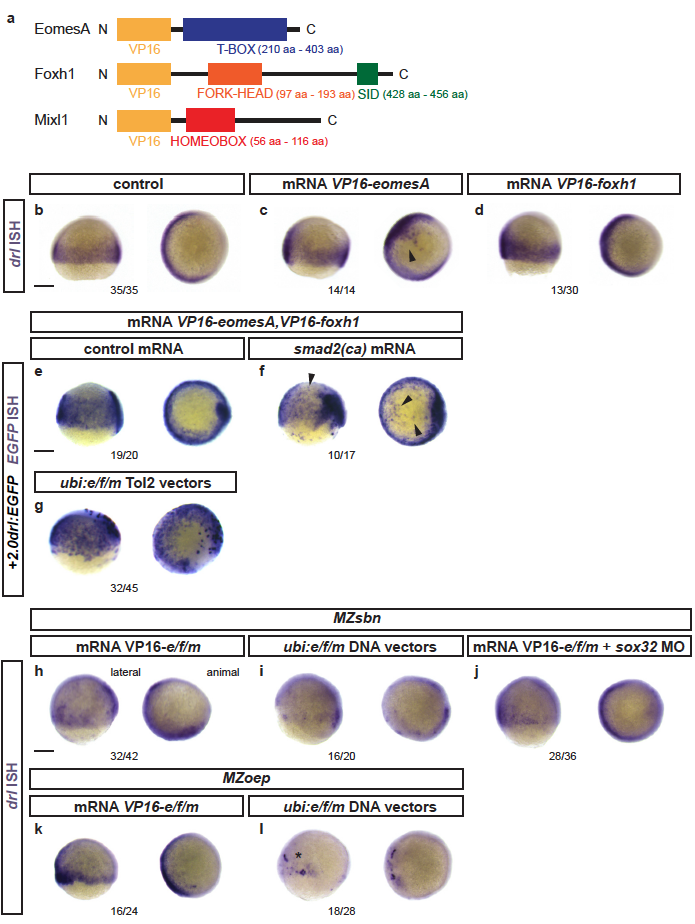
Fig. S5
Response of endogenous drl and drl reporters to EomesA, Foxh1, and Mixl1 expression
(a) Schematics of EomesA, Foxh1, and Mixl1 fusion proteins with the N-terminally added VP16 transactivation domain to generate constitutively-active transcription factors. Note that the expressed VP16-EomesA is restricted to the T-box of EomesA. (b-d) mRNA ISH for endogenous drl expression in controls (n=35/35) (b) and embryos injected with VP16-fusions based on eomesA (n=14/14) (c) or foxh1 (n=13/30) (d). (e,f) mRNA ISH for EGFP transcript expression in +2.0drl:EGFP embryos at shield to 70% epiboly stage after injecting a combination of VP16-fused eomesA and foxh1 (e/f) without (n=19/20) (e) or with (n=10/17) (f) constitutive-active smad2 that mimicks pan-Smad signaling (smad2(ca)), resulting in dorsal widening of the reporter expression pattern. (g) Injection of Tol2-based constructs under ubiquitous ubi promoter control to drive native eomesA (full-length), foxh1, and mixl1 (e/f/m), resulting in mosaic induction of +2.0drl:EGFP, including individual dorsal blastomeres (n=32/45). (h-j) Endogenous drl expression revealed by mRNA ISH in BMP signaling-mutant (MZsbn) embryos injected with either (h) VP16-e/f/m mRNA (n=32/42), (i) ubi:e/f/m DNA vectors (n=16/20), or (j) VP16-e/f/m mRNA in an endoderm-perturbed background (sox32 morpholino) (n=28/36). (k,l) mRNA ISH for endogenous drl expression in Nodal-mutant (MZoep) embryos injected with (k) VP16-e/f/m mRNA (16/24) or (l) ubi:e/f/m Tol2 vectors (17/28); note the localized clones of strong drl upregulation on the ventral side upon ubi:e/f/m injection. Scale bar 250 μm.