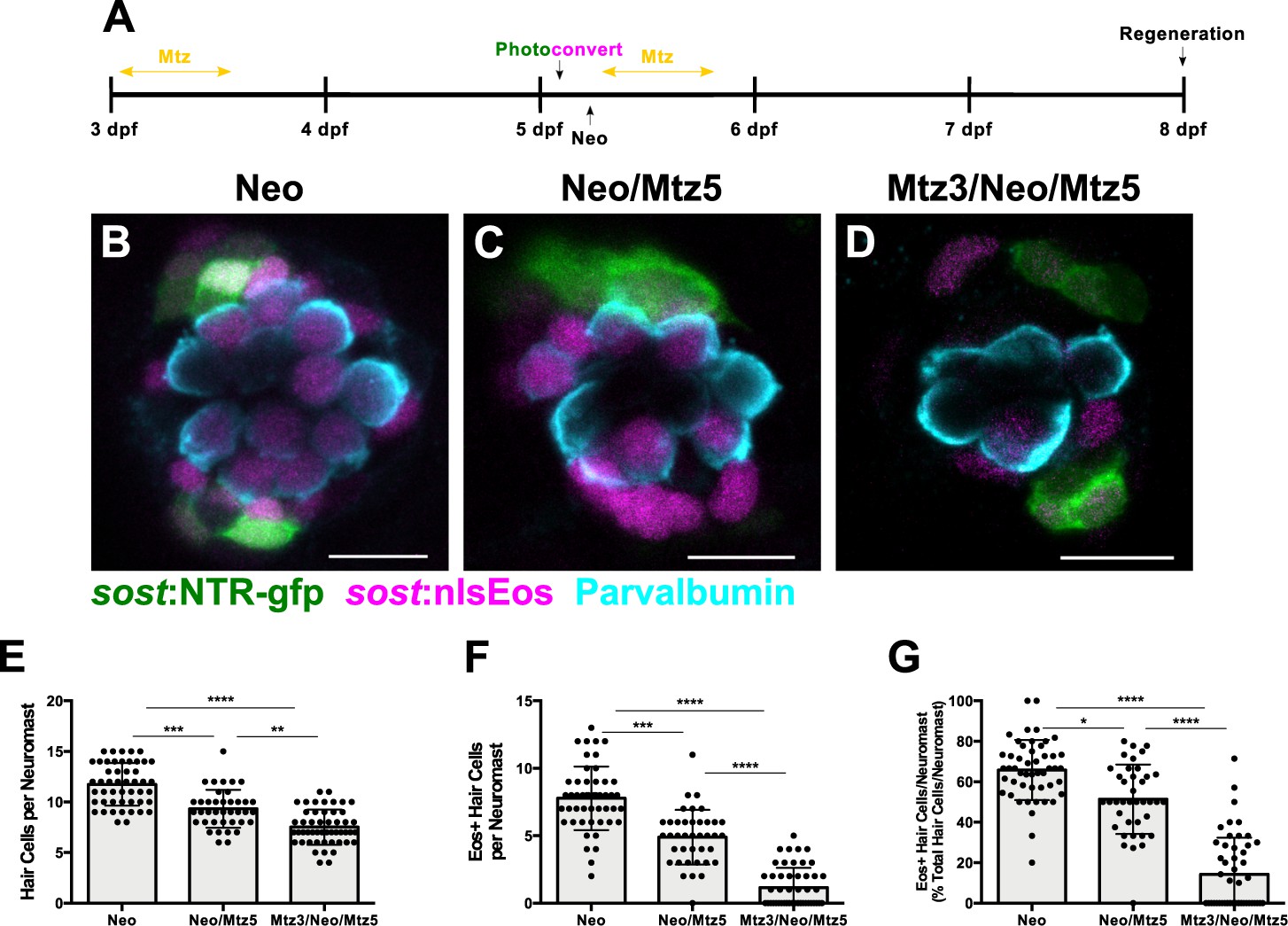
Fig. 6
Ablation of DV cells decreases number of regenerated hair cells.
(A) Timeline of DV cell-ablation experiment. Larvae were treated with Mtz at 3 dpf, photoconverted, then treated with neomycin, then treated with Mtz again at 5 dpf, and fixed and immunostained at 72 hpt (8 dpf). (B–D) Maximum projections of neuromasts from sost:NTR-GFP; sost:nlsEos fish following neomycin (B; Neo), neomycin and Mtz (C; Neo/Mtz5), and Mtz, neomycin, and Mtz treatments (D; Mtz3/Neo/Mtz5). Sost:NTR-GFP cells are shown in green, sost:nlsEos cells are shown in magenta, and anti-Parvalbumin-stained hair cells are shown in cyan. Scale bar = 10 μm. (E) Total hair cells per neuromast following regeneration. Neo: 11.73 ± 2.10, n = 49 neuromasts (10 fish); Neo/Mtz5: 9.33 ± 1.88, n = 39 neuromasts (8 fish); Mtz3/Neo/Mtz5: 7.52 ± 1.74, n = 50 neuromasts (10 fish); mean ± SD; Kruskal-Wallis test, Dunn’s post-test, p=0.0001 (Neo vs. Neo/Mtz5), p<0.0001 (Neo vs. Mtz3/Neo/Mtz5), p=0.0016 (Neo/Mtz5 vs. Mtz3/Neo/Mtz5). (F) Sost:nlsEos-positive hair cells per neuromast following regeneration. Neo: 7.78 ± 2.36, n = 49 neuromasts (10 fish); Neo/Mtz5: 4.90 ± 2.02, n = 39 neuromasts (eight fish); Mtz3/Neo/Mtz5: 1.16 ± 1.46, n = 50 neuromasts (10 fish); mean ± SD; Kruskal-Wallis test, Dunn’s post-test, p=0.0003 (Neo vs. Neo/Mtz5), p<0.0001 (Neo vs. Mtz3/Neo/Mtz5, Neo/Mtz5 vs. Mtz3/Neo/Mtz5). (G) Percentage of hair cells per neuromast labeled by sost:nlsEos following regeneration. Neo: 65.81 ± 14.89, n = 49 neuromasts (10 fish); Neo/Mtz5: 51.40 ± 17.17, n = 39 neuromasts (8 fish); Mtz3/Neo/Mtz5: 14.29 ± 18.10, n = 50 neuromasts (10 fish); mean ± SD; Kruskal-Wallis test, Dunn’s post-test, p=0.0147 (Neo vs. Neo/Mtz5), p<0.0001 (Neo vs. Mtz3/Neo/Mtz5, Neo/Mtz5 vs. Mtz3/Neo/Mtz5).