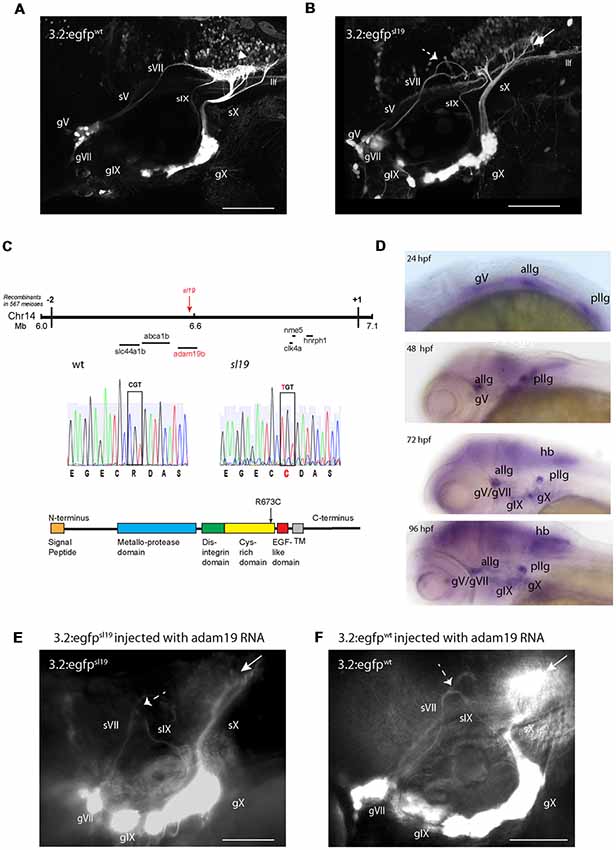
Fig. 1
Characterization of the sl19 mutant line. (A) Wild type larva at 4 days post fertilization (4 dpf) showing normal pattern of cranial sensory ganglia (CSG) projections. sV (also llf-lateral longitudinal fascicle), sVII, sIX and sX are the projections of the trigeminal (gV), facial (VII), glossopharyngeal (IX) and vagus (X) ganglia, respectively. White arrowhead shows normal hindbrain plexus, where sVII, sIX and sX sensory axons terminate. (B) CSG projections in a 4dpf sl19 mutant. White arrow indicates malformed hindbrain plexus and dotted arrow shows the misrouted and defasciculated sVII failing to terminate in the plexus. sIX and sX fail to form normal terminal fields. Projections from gV appear normal. (C) Positional cloning of sl19. The lesion was mapped to a critical region on chromosome 14 between 6 and 7 Mb. Transcripts of all genes in this region (20 in total) were sequenced (for clarity, only some of these genes are shown in the Figure). Only the adam19b gene showed an altered coding sequence—a single base mutation in exon 17. This C > T conversion causes an arginine to cysteine switch at amino acid 673 in the cysteine-rich domain (CRD) of A Disintegrin and Metalloproteinase (ADAM) 19b (CRD). (D) Wholemount in situ hybridization (ISH) of adam19b in the zebrafish head. At 24 hpf, adam19b is expressed in the trigeminal ganglion (gV), the anterior lateral line ganglion (allg) and the posterior lateral line ganglion (pllg). At 48 hpf, expression has expanded to include regions of the hindbrain. By 72 hpf, adam19b is also expressed in the epibranchial ganglia (gVII, gIX and gX) and in the hindbrain (hb); by 96 hpf, expression has increased in all these cranial structures. Sense probe did not produce staining at any time point (data not shown). (E) adam19b full length RNA injected into sl19 mutant. Over-expression of adam19b did not rescue the mutant phenotype, but resulted in a higher incidence of the mutant phenotype (see text). White arrow indicates malformed plexus; dotted arrow shows misrouted sVII and sIX. (F) adam19b full length RNA injected into wild type. As can be seen, over-expression of adam19b induced aberrant epibranchial projections in 4 dpf wild type fish, identical to that found in the sl19mutant. White arrow: malformed plexus, showing how sX forms a dense clump of axons, instead of the organized branching of the axons seen in un-injected controls (A). Dotted arrow: misrouted sVII and sIX. Panels (A,B) are confocal z-stacks, panels (E,F) are epifluorescent micrographs. All images are oriented anterior to the left and dorsal at top. Scale bars = 100 μm.