Fig. 4
CNE1 mediates direct autoregulation and positive feedback via a paired domain binding site.
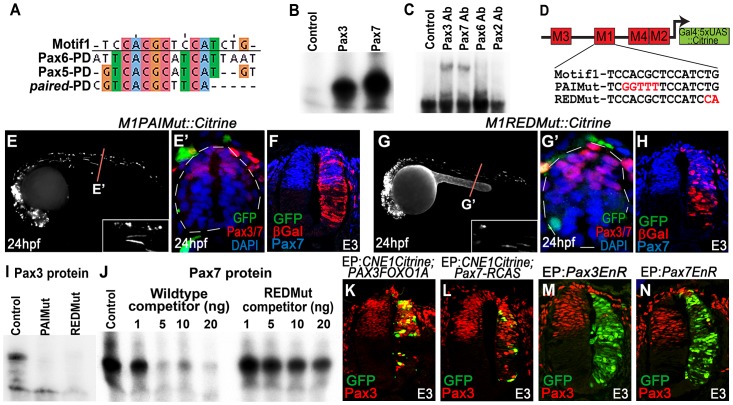
(A) CNE1-Motif1 is homologous to the 5′ region of defined PD binding sites, however the alignment diverges in the 3′ region. (B) EMSA performed using Motif1 DNA and in-vitro synthesised Pax3 and Pax7 proteins, both of which can bind the sequence. (C) EMSA using Motif1 DNA and chick spinal cord nuclear extract, addition of antibodies against Pax3 or Pax7 to the reaction decreases the mobility of the DNA/protein complex. Addition of Pax6 or Pax2 antibodies does not alter the distribution of complexes within the EMSA. (D) Schematic illustrating the mutations targeted within CNE1-Motif1. (E, E′) M1PAIMut transgenic zebrafish exhibit a marked reduction in CNE1 activity in spinal cord progenitors, compared to the wildtype enhancer (n = 2/38, p<0.001). (F) Mutation of the PAI domain binding site precludes CNE1 activity in the chick neural tube (n = 0/8, p = 0.0007). (G, G′) Mutation of the RED domain binding site phenocopies Motif1 deletion in zebrafish embryos (n = 0/19, p<0.001) and chick embryos (H) (n = 1/5, p = 0.0128). (I) EMSAs performed using in vitro synthesised Pax3 protein and Motif1 DNA harboring either PAI or RED mutations. Mutation of either PAI or RED region precludes complex formation. (J) Competition EMSA performed using in vitro synthesised Pax7 protein, radiolabelled wildtype Motif1 DNA and non-labeled competitor probes. Non-labeled wildtype DNA effectively competes with radiolabelled probe for Pax7 binding, whereas DNA harboring the RED mutation cannot. (K) Electroporation of PAX3FOXO1A-RCAS induces ectopic CNE1 activity and Pax3 protein expression in the ventral neural tube (n = 9). (L) Pax7-RCAS electroporation also induces CNE1 activity and Pax3 expression (n = 7). Electroporation of dominant negative forms of Pax3 (M) (n = 7) or Pax7 (N) (n = 6) represses Pax3 protein expression within its endogenous domain.