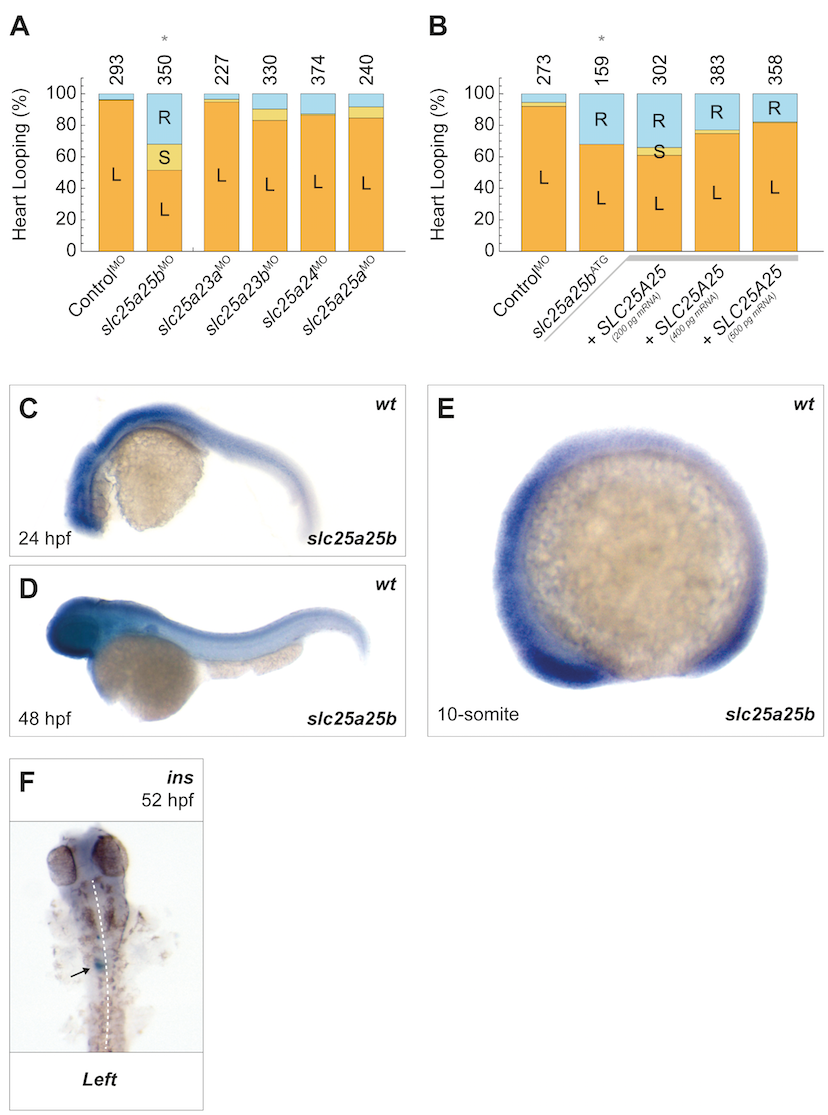
Fig. S5
Loss of slc25a25b expression in zebrafish caused randomization of left–right patterning.
(A) SCaMC has 3 homologs in vertebrates SLC25A23, SLC25A24, and SLC25A25. In zebrafish, these proteins are encoded by slc25a23a, slc25a23b, slc25a24, slc25a25a, and slc25a25b. MO-induced knockdown of slc25a25b caused randomized heart looping in zebrafish (slc25a25bMO; *P = 1.1 × 10−34). (B) Similar to splice-blocking slc25a25bMO, translation-blocking slc25a25bATG MOs induced randomization of heart looping in zebrafish embryos (*P = 3.2 × 10−13). Similar to D. melanogaster (Fig 2E), this phenotype was rescued by injection (+) of human SLC25A25 mRNA in a concentration-dependent fashion (+SLC25A25). (C) In situ hybridization of slc25a25b mRNA in wild-type zebrafish 24 hpf, (D) 48 hpf, and (E) at 10-somite stage. (F) Lateral pancreas placement—visualized by in situ hybridization of preproinsulin (ins)—was altered in slc25a25b morphants, highlighting a general heterotaxy defect 52 hpf (n = 28; left = 10; center = 14; right = 4; in comparison to ControlMO: n = 24; left = 2; center = 10; right = 12; *P = 0.002). Numbers of embryos are indicated above bars. L = left; S = symmetric; R = right. For numerical values, see S1 Data. hpf, hours post fertilization; MO, Morpholino-oligonucleotide; SLC25A25, solute carrier 25 A 25.