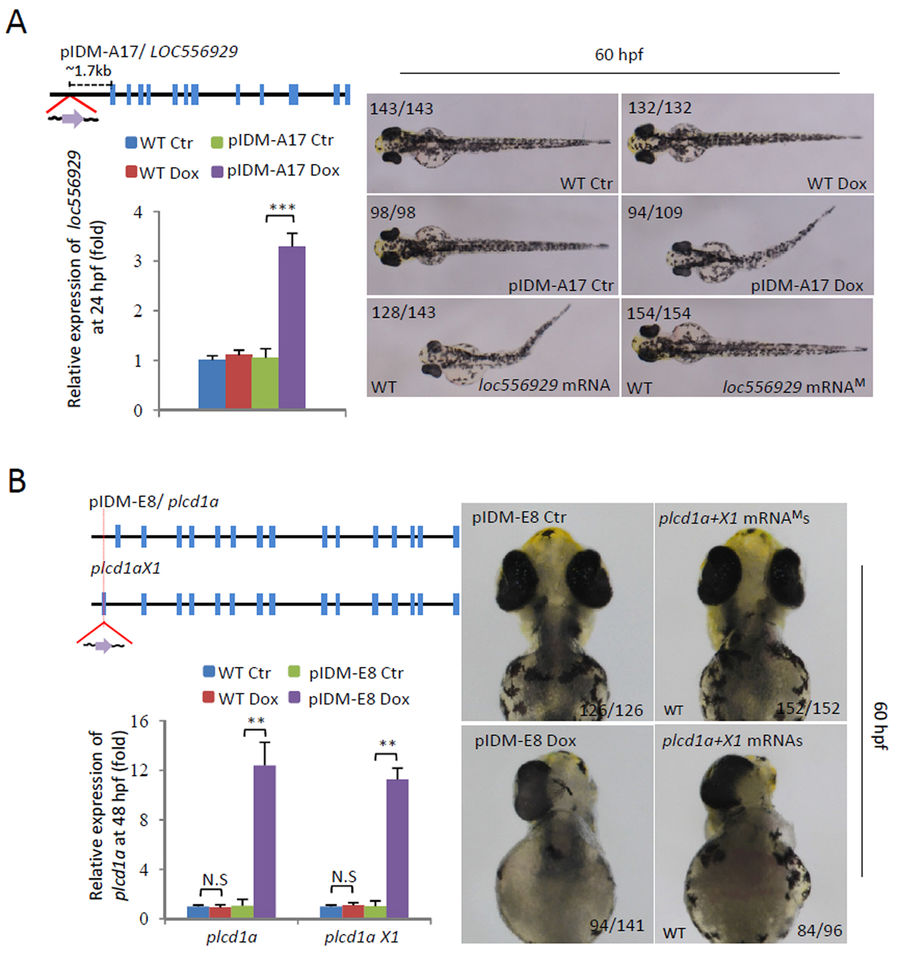
Fig. 3
Dox-dependent up-regulation of genes in two example mutants causes abnormal embryonic development. (A) Line pIDM-A17. Upper left panel: Diagram showing the position and orientation of pIDM in loc556929 genomic DNA. Bottom left panel: The relative expression level of the loc556929 transcript upon Dox-treatment was analyzed at 24 hpf. Right panel: Pictures of WT and mutant embryos with different treatments at 60hpf as indicated, noting that over-expression of wild-type loc556929 mRNA, but not mutant loc556929 mRNAM, phenocopied embryonic defects in pIDM-A17 transgenic embryos after Dox induction. (B) Line pIDM-E8. Upper left panel: Diagram showing the position and orientation of pIDM in the plcd1a genomic DNA (including two isoforms plcd1a andX1). Bottom left panel: The relative expression levels of plcd1a and X1 transcripts upon Dox-treatment was analyzed with specific primers at 48 hpf. Right panel: Pictures of WT and mutant embryos with differing treatments at 60 hpf as indicated, noting that over-expression of wild-type plcd1a + X1 mRNAs, but not plcd1a + X1 mRNAMs, phenocopied embryonic defects including a single eye in pIDM-E8 transgenic embryos after Dox treatment. In A and B, representative embryos are shown, the number of embryos showing the displayed phenotype versus total embryos examined are provided in the corresponding panels.