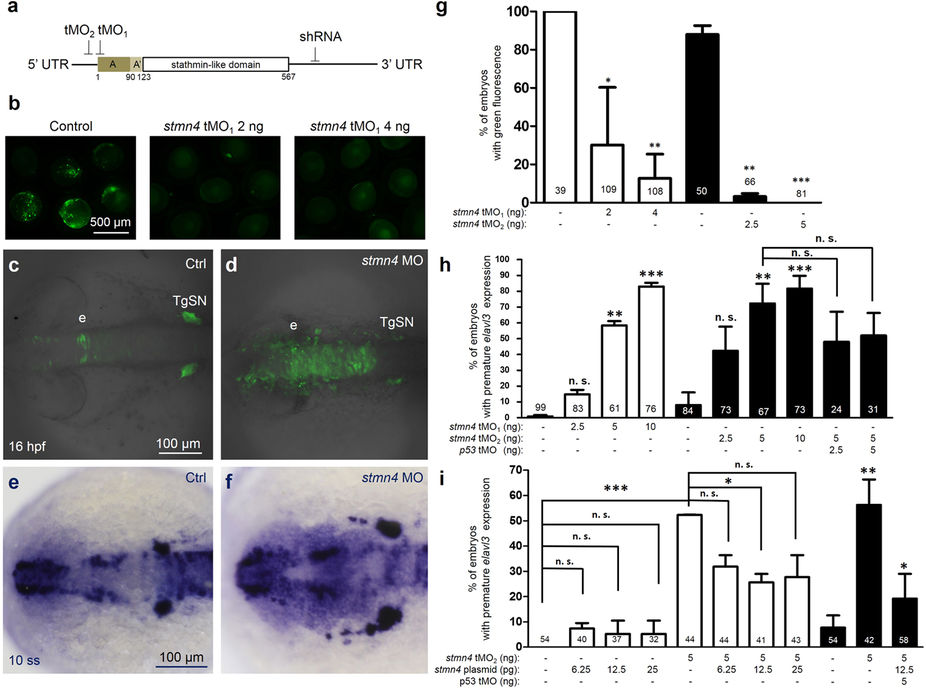
Fig. 2
stmn4 knockdown resulted in premature expression of elavl3 in zebrafish embryos.
(a) Target sites are indicated for two antisense translational blocking morpholino oligo nucleotides (tMO1 and tMO2) and one small hairpin RNA (shRNA) at the start codon, 5′ and 3′ untranslated region (UTR), respectively. (b) Embryos were injected with 200 pg of PCS2+ vector with an insertion of a fragment of stmn4 containing both tMO1 and tMO2 binding sites as indicated in (a) without (control) or with tMO1 or tMO2 (stmn4 MO) as indicated, examined and photographed at the bud stage. The percentages of embryos with green fluorescence were calculated and compared to the control groups as shown in (g). Tg(Huc:kaede) embryos were injected without (c, Ctrl) or with different amounts of stmn4 tMO1 or tMO2 (d, stmn4 MO), P53 MO and stmn4 expression vectors, cultured to 16 hpf and examined under confocal microscopy. A stack of 10 layers (2.5 μm for one layers) from the top of midbrain were combined and shown. (e–i) Wild type embryos were treated as described previously, cultured to 10-somite stage, fixed and subjected to WISH against elavl3. Representative photographs are presented (e,f). Scale bars are only shown on the left panel in a row. A premature elevation of elavl3 expression was observed in embryos injected with stmn4 MO (f) compared that of control. The percentages of embryos with elevated elavl3 expression in the dorsal midbrain were calculated and shown in (g–i). Photographs are at the same scale in each row and scale bars are only shown in the left panels. Experiments were repeated three times. Data was analyzed by one-way ANOVA and presented as mean +/−s.e.m. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.005, ***P < 0.0005. The numbers of embryos used are shown at the top or bottom of each bar.