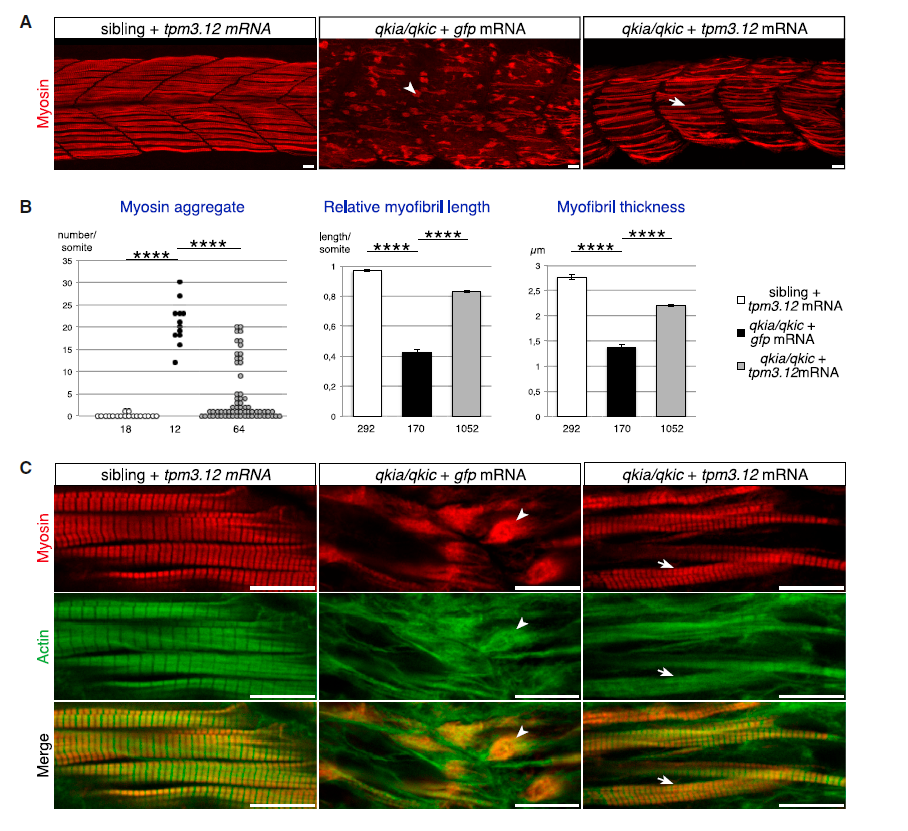
Fig. 6
Tpm3.12 Restores Myofibril Formation in qkia/qkic Embryos
Embryos from intercrosses of qkia+/− parents were injected with qkic MO in combination with GFP or tpm3.12 mRNA.
(A) Confocal imaging of myosin-immunostained 26-hpf zebrafish embryos (lateral view with z projection). In qkia/qkic embryos overexpressing GFP (n = 11), strong myofibril defects such as myosin aggregates (arrowhead) are observed. Injection of tmp3.1 mRNA in sibling embryos (n = 99) does not affect myofibril development whereas in qkia/qkic embryos (n = 33), it rescues the formation of myofibrils in most muscle cells (arrow).
(B) Quantification of the myofibril phenotype illustrated in (A). All qkia/qkic embryos injected with tpm3.12 mRNA somite (n = 21) have significantly less myosin aggregate per somite (Student's t test, p = 3.5 × 10−9), as well as longer and thicker myofibrils (Student's t test, p = 2.7 × 10−27 and 2.2 × 10−7, respectively) compared with qkia/qkic embryos injected with GFP mRNA (n = 4), albeit less long and thick than myofibrils of sibling embryos injected with GFP mRNA (n = 4). Numbers under the graph indicate the total number of quantified somites (left graph) and myofibrils (right and middle graphs). Pooled data are presented as mean ± SEM. ns, not significant.
(C) Confocal imaging of myosin (red) and actin (green) immunostained 26-hpf zebrafish embryos (single optical section). In qkia/qkic embryos overexpressing GFP, numerous myosin and actin aggregates (arrowheads) are observed. Injection of tmp3.1 mRNA into sibling embryos does not affect myofibril development whereas in qkia/qkic embryos, it rescues the formation of myofibrils, which display the typical striated pattern of actin and myosin (arrows).
In all panels, anterior is to the left. ∗∗∗∗p < 1 × 10−4. Scale bars, 10 μm.
Reprinted from Developmental Cell, 42(5), Bonnet, A., Lambert, G., Ernest, S., Dutrieux, F.X., Coulpier, F., Lemoine, S., Lobbardi, R., Rosa, F.M., Quaking RNA-Binding Proteins Control Early Myofibril Formation by Modulating Tropomyosin, 527-541.e4, Copyright (2017) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Cell