Fig. 3
qkia and qkic Control Nascent Myofibril Formation through Myosin Filament Assembly
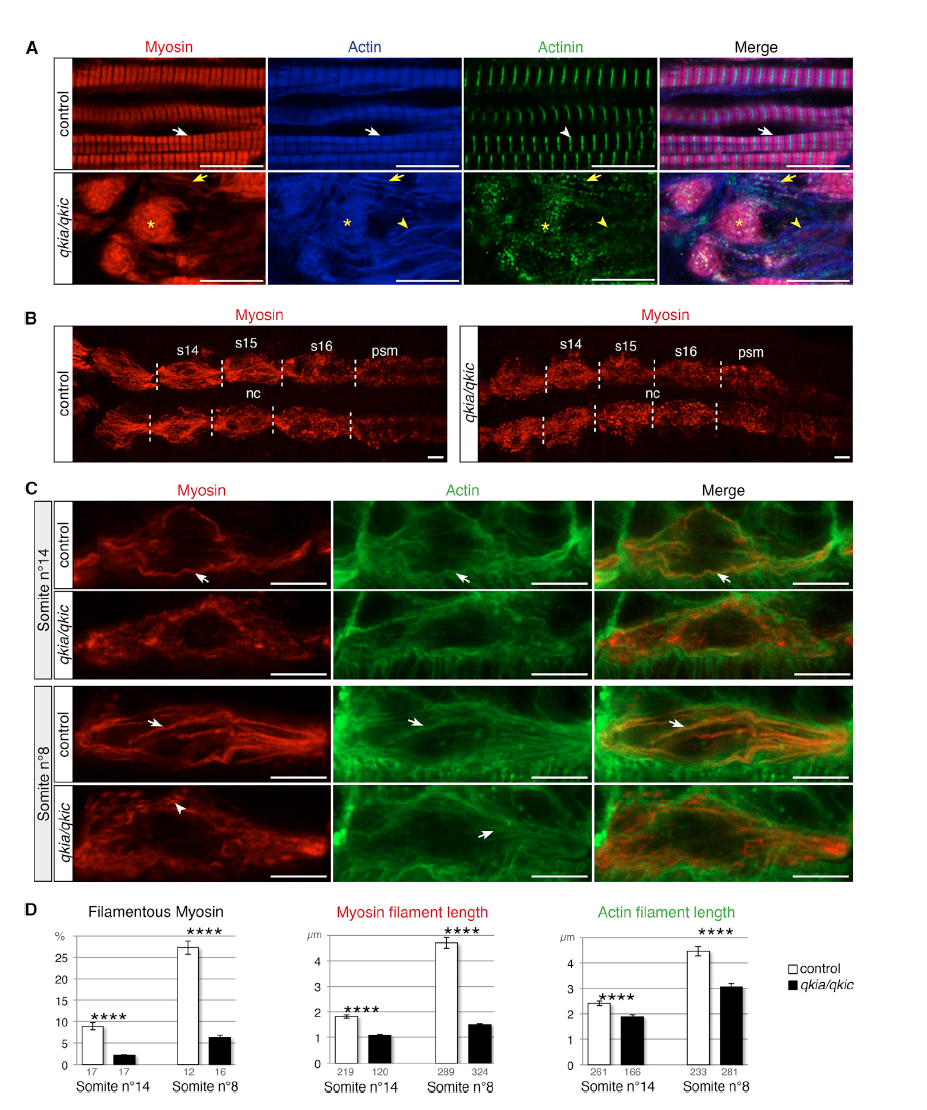
(A) qkia and qkic control sarcomere formation. Confocal imaging of myosin (red), actin (blue), and actinin (green) immunostaining at 26 hpf (lateral view from single optical sections). Slow muscle myofibrils in control embryos (WT or qkia+/− embryos injected with control MO) (n = 46) display the typical actin and myosin striated pattern (white arrows) with sharp bands of actinin (white arrowhead). Slow muscle cells in qkia/qkic embryos (qkia−/− embryos injected with qkic MO) (n = 33) contain myosin/actin aggregates (asterisks) decorated with actinin dots, myosin/actin filaments also decorated with actinin dots (yellow arrows), and actin filaments devoid of myosin (yellow arrowheads).
(B and C) qkia and qkic control myosin filament assembly in early differentiating slow muscle cells. Confocal imaging of myosin (red) and actin (green) immunostaining at 17 hpf (16-somite stage) in control (WT or qkia+/− embryos injected with control MO) and qkia/qkic embryos (qkia−/− embryos injected with qkic MO), dorsal view. (B) View of all slow muscle cells in posterior somites (z projection). Somites 14 to 16 (s14–s16) borders are indicated by dashed lines. nc, notochord; psm, pre-somitic mesoderm. (C) Focus on one slow muscle cell (single optical section). In control embryos (n = 10), myosin and actin gradually organize into long filamentous structures (arrows), prefiguring slow muscle differentiated myofibrils. In qkia/qkic embryos (n = 13), actin retains the capacity to form filamentous structures (arrows) while myosin instead forms short stretches (arrowhead) or remains diffuse.
(D) Quantification of the myofibril phenotype illustrated in (C). At 14th somite level, in qkia/qkic embryos (n = 5), myosin and actin filaments are significantly shorter (Student's t test, p = 4 × 10−17 and 3 × 10−6, respectively) and myosin is less condensed into filaments (Student's t test, p = 5 × 10−8) compared with control embryos (n = 5). In more differentiated cell (eighth somite level), in qkia/qkic embryos (n = 4) myosin and actin filaments are still significantly shorter (Student's t test, p = 6 × 10−40 and 4 × 10−10, respectively) and myosin is less condensed (Student's t test, p = 1 × 10−8) compared with control embryos (n = 4). Numbers under the graph indicate the total number of quantified sections (left graph) and myosin and actin filaments (middle and right graph). Data are presented as mean ± SEM.
In all panels, anterior is to the left. ∗∗∗∗p < 1 × 10−4. Scale bars, 10 μm.
Reprinted from Developmental Cell, 42(5), Bonnet, A., Lambert, G., Ernest, S., Dutrieux, F.X., Coulpier, F., Lemoine, S., Lobbardi, R., Rosa, F.M., Quaking RNA-Binding Proteins Control Early Myofibril Formation by Modulating Tropomyosin, 527-541.e4, Copyright (2017) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Cell