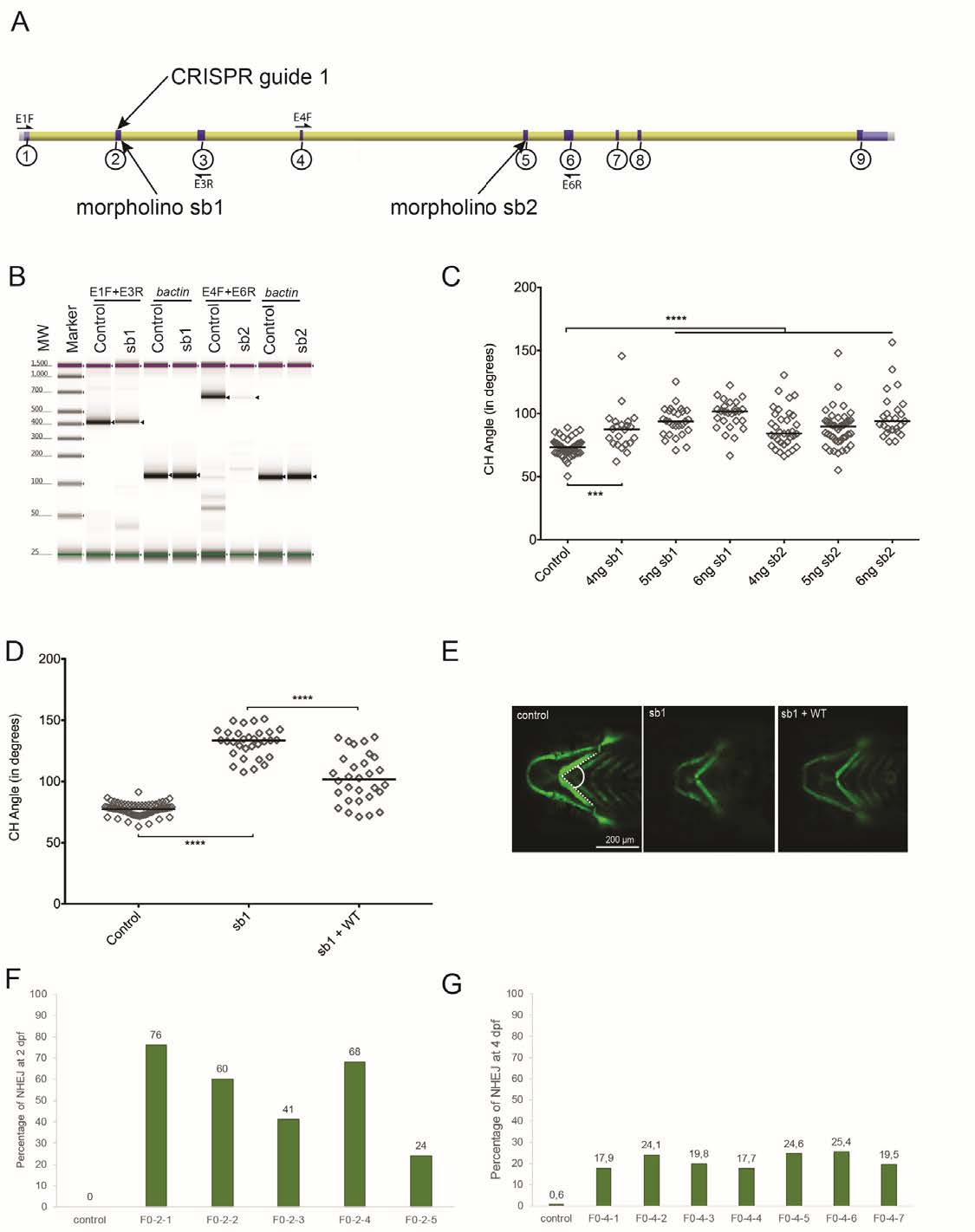
Fig. S4.1
Efficiency of morpholinos (MOs) and CRISPR sgRNA targeting cep55l. (A) Schematic of the Danio rerio cep55l locus showing the location of the two MOs and the CRISPR guide target sites. Exons are indicated with circled numbers. (B) TapeStation electrophoresis of RT-PCR products showing sb1 and sb2 morpholino efficiency. Sequencing of cloned PCR fragments showed that sb1 produces a 45 bp retention of intronic sequence, and sb2 results in deletion of 242 bp; both result in premature termination codons. Expected bands are indicated with black arrows; primer locations are indicated in panel A; [sic]-actin was amplified to control for cDNA integrity. (C) Dose curve of sb1 and sb2 MOs. Embryo batches were injected with increasing amounts of MO, imaged live at 4 dpf, and the angle of the ceratohyal (CH) cartilage was measured (See panel E); n=22-59 embryos/injection. (D) Plot representing the effects of sb1 and sb1 + WT-RNA injections on 4 dpf -1.4col1a1:egfp larvae. sb1 induces a significant increase in the CH angle compared to uninjected controls. Co-injection of WT-RNA with sb1 rescues significantly the CH angle. n= 20-63 embryos/injection, repeated. (E) Representative live ventral images of 4 dpf -1.4col1a1:egfp larvae demarcate cartilage structures with the presence of GFP-positive cells. CH angle was measured as shown (dashed white lines). (F) Estimation of mosaicism in cep55l F0 mutant embryos harvested at 2 dpf as assessed by cloning of PCR products flanking the targeting site and Sanger sequencing. (G) Assessment of CRISPR/Cas9 genome editing efficiency using next generation sequencing of PCR products amplified from genomic DNA of control and cep55l F0s (n=7) harvested at 4 days post fertilization. NHEJ, nonhomologous end joining; **** indicates p<0.0001.