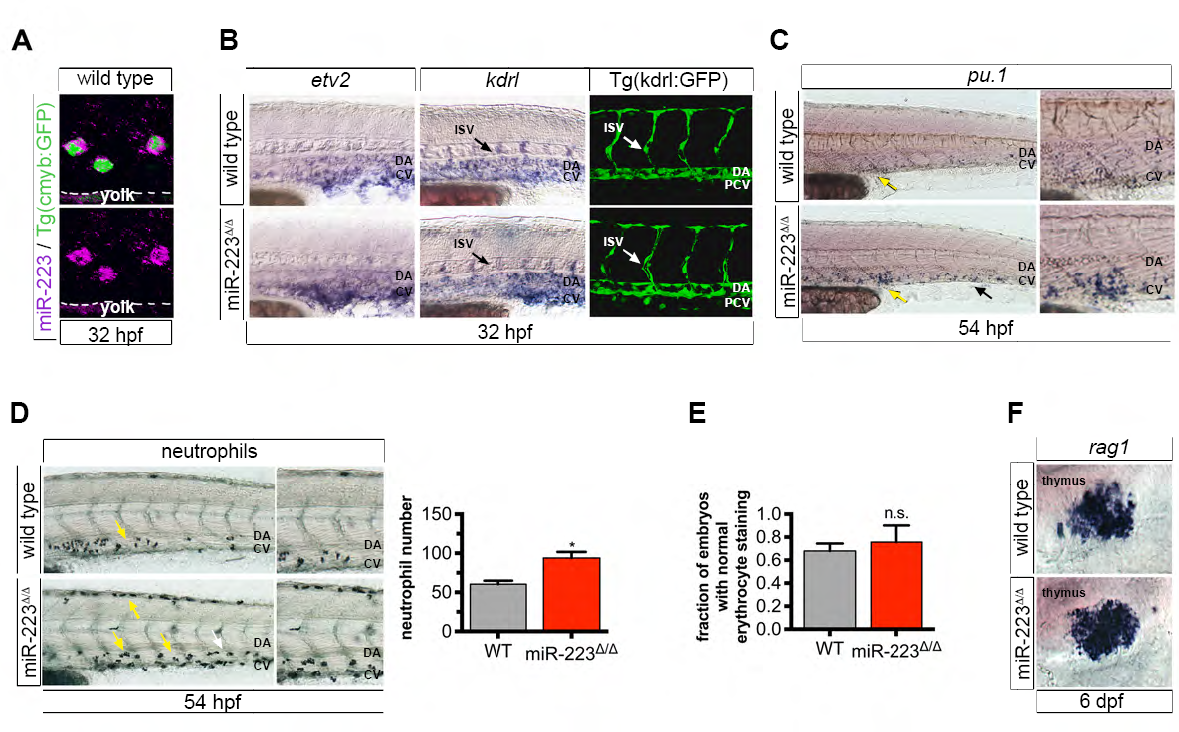
Fig. S5
S5. miR-223Δ/Δ embryos have a specific defect in HSPC formation and neutrophil differentiation (related to Figure 5).
(A) Confocal projection showing the localization of miR-223 WISH in cmyb:GFP+ HSPCs in the vasculature above the yolk extension.
(B) WISH localization of vascular angiogenesis markers and vessel morphology revealed by Tg(kdrl:gfp)la116. Arrows show positively stained ISVs. No differences were detected between wild type and mutant embryos, suggesting that HSPC expansion in miR-223Δ/Δ is specific defect in HSPC production, and not a secondary consequence of abnormal vascular patterning.
(C) miR-223Δ/Δ embryos exhibited an increase in pu.1+ myeloid progenitors by WISH in the caudal hematopoietic tissue (arrows), a transient site of hematopoiesis in the tail. Yellow arrows point to the region captured in magnified images.
(D) Sudan black-stained neutrophils were increased in miR-223Δ/Δ embryos in CHT. Arrows point to positively stained cells. Yellow arrows point to the region captured in zoomed-in images. Bar plots show average of replicate means + SEM of neutrophil number. Significant difference *p ≤ 0.05 from wild type was determined by two-tailed Mann-Whitney U-test (n = 5 replicates of 10 embryos).
(E) Quantification shows the fraction of embryos with normal o-dianisidine staining of erythrocytes at 32 hpf. Bars show average of replicate means + SEM. Erythrocyte staining was not statistically different (n.s., p > 0.05) to wild type embryos by two-tailed Mann- Whitney U-test (n = 3 replicates of 9-10 embryos).
(F) Lymphocyte marker rag1 was unaffected upon loss of miR-223 as determined by WISH. For WISH and immunofluorescence experiments, n = 10-20 embryos.
Reprinted from Developmental Cell, 40, Kasper, D.M., Moro, A., Ristori, E., Narayanan, A., Hill-Teran, G., Fleming, E., Moreno-Mateos, M., Vejnar, C.E., Zhang, J., Lee, D., Gu, M., Gerstein, M., Giraldez, A., Nicoli, S., MicroRNAs Establish Uniform Traits during the Architecture of Vertebrate Embryos, 552-565.e5, Copyright (2017) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Cell