Fig. 1
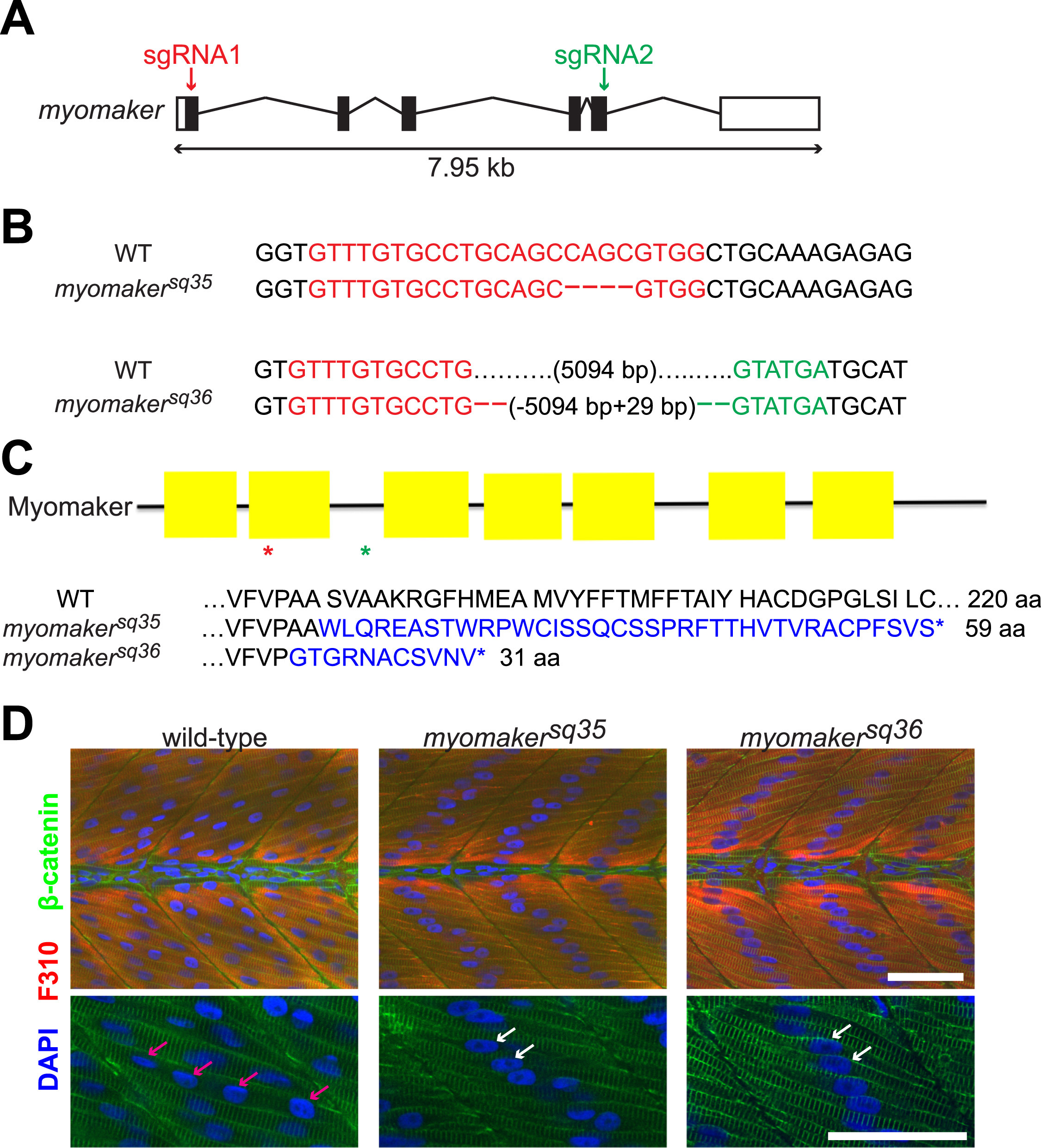
Myomaker mutants are defective in myocyte fusion. A: Schematic diagram of myomaker gene structure. White and black boxes represent UTRs and exons respectively, and the lines indicate introns. The arrows indicate regions targeted by sgRNAs. B: Sequences of wild-type and myomaker alleles showing the mutations. Deleted bases are shown as dashes, while sgRNA1 and sgRNA2 target regions are shown in red and green respectively. C: Diagram of Myomaker protein structure and predicted protein sequences of myomaker alleles. The yellow boxes in the diagram represent the transmembrane domains, while the red and green asterisks indicate the premature STOP codon positions of the myomakersq36 and myomakersq35 mutant proteins respectively. For the protein sequences, the sequences in blue are those that are different from wild-type sequence. D: Fast-twitch muscle cells of 2 d.p.f. myomaker mutant embryos are mostly mononucleated, unlike the multinucleated fast-twitch muscle cells of wild-type embryos. Fast-twitch muscle cells are labeled with F310 antibody, with the nuclei and cell membranes stained with DAPI and anti-β-catenin antibodies, respectively. The bottom panel shows magnified images of a few muscle cells from the top panel. The pink arrows indicate the multiple nuclei within a wild-type muscle cell, while the white arrows indicate the single nuclei of mononucleated mutant muscle cells. Scale bar=50 µm.
Reprinted from Developmental Biology, 423(1), Zhang, W., Roy, S., Myomaker is required for the fusion of fast-twitch myocytes in the zebrafish embryo, 24-33, Copyright (2017) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Biol.