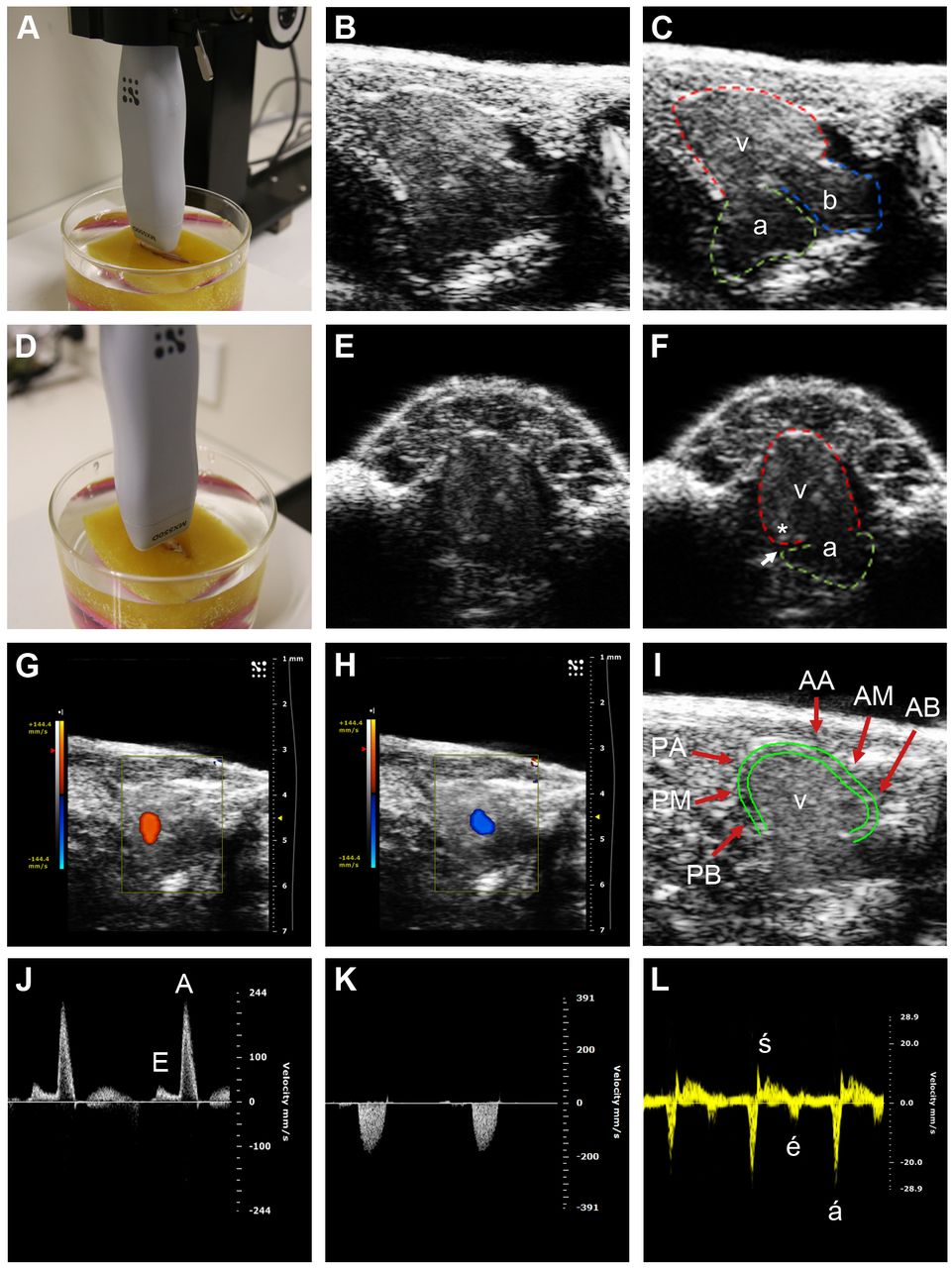
Fig. 1
Zebrafish echocardiographic imaging. (A) Transducer position for the longitudinal axis (LAX) view. (B,C) LAX images, with ventricle (v, red tracing denotes epicardium), atrium (a, green tracing) and bulbus arteriosus (b, blue tracing) indicated in C. (D) Transducer position for the short axis (SAX) view. (E,F) SAX images, with ventricle and atrium indicated in F. The ventricle joins the atrium at the atrioventricular annulus, with the atrioventricular groove (white arrow) overlying this area. An asterisk labels the area of myocardium immediately adjacent to atrioventricular annulus which is the site of tissue Doppler interrogation. (G,H) Color Doppler in the LAX view showing (G) ventricular inflow (orange) from the atrium during ventricular diastole, and (H) ventricular outflow (blue) to the bulbus arteriosus during ventricular systole. (I) Ventricular wall motion was analyzed in six segments: AA, anterior (ventral) apex; AM, anterior mid; AB, anterior base; PA, posterior (dorsal) apex; PM, posterior mid; PB, posterior base. The epicardium (outer green border) and the inner border of the compact myocardium (inner green border) of the ventricle are shown. (J) Pulsed-wave Doppler interrogation of atrioventricular inflow at the level of the atrioventricular valve, showing the E (early diastolic) and A (atrial systolic) waves. (K) Pulsed-wave Doppler interrogation of ventricular outflow. (L) Tissue Doppler interrogation of the atrioventricular annulus demonstrating the é (early diastolic), á (atrial systolic) and ś (ventricular systolic) waves.