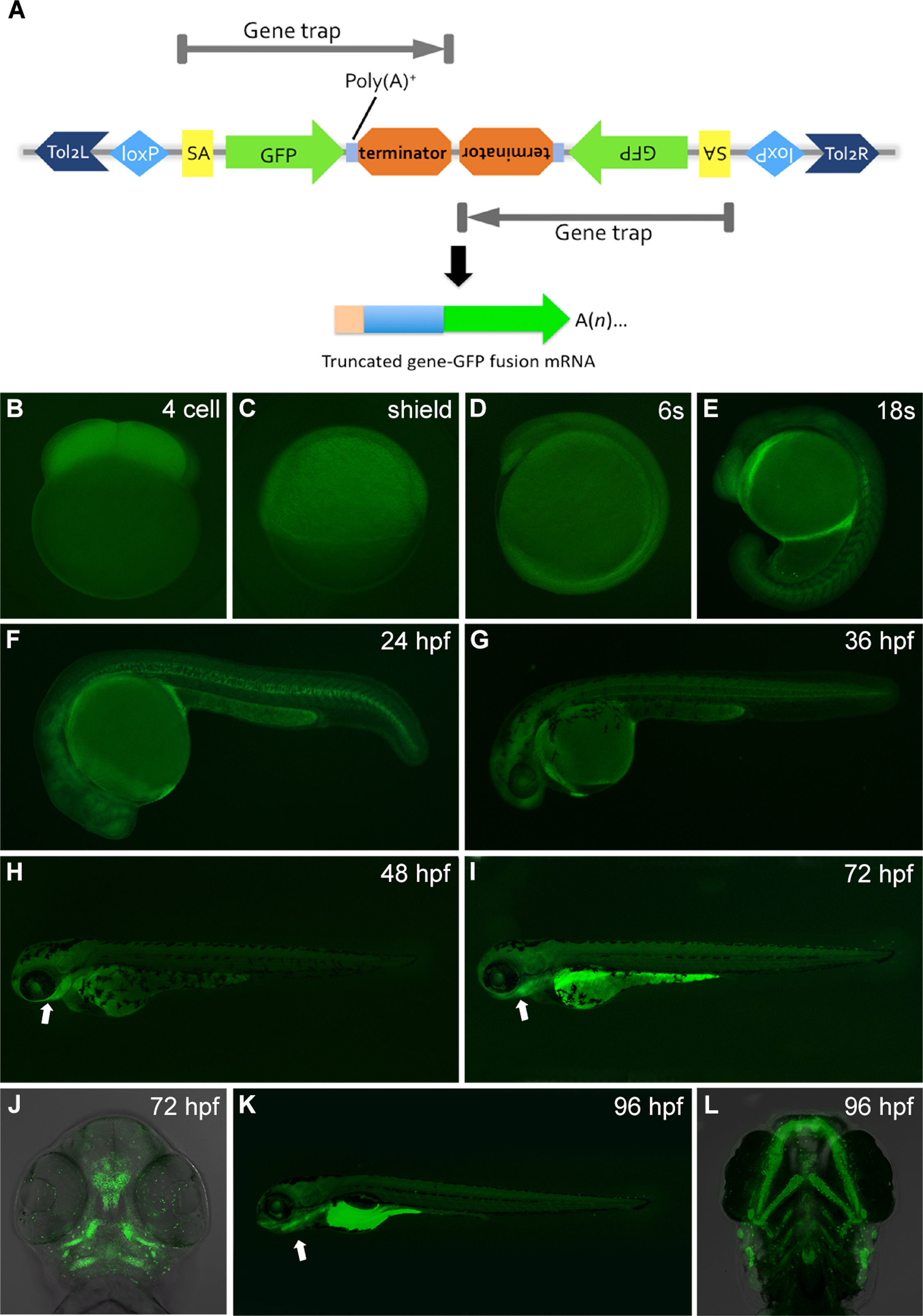
Fig. 1
Gene trapping construct and GFP expression pattern of gene trap line RP24-104 during embryogenesis. (A) Schematic of RP-T gene trapping construct. RP-T transposon system composed of two protein-trap cassettes with a transcriptional stop in the opposite direction. Tol2L and Tol2R, tol2 transponase inverted terminal repeat; SA, splice acceptor; GFP, AUG-less monomeric GFP sequence; poly(A)+, polyadenylation signal; terminator, transcriptional border element. (B–L) GFP expression pattern in zebrafish gene trap line RP24-104. Prior to 16-somite stage, GFP signal could be observed in the whole embryo (B to D). From 16-somite stage, elevated signal could be observed in notochord on the ubiquitous GFP expression background (E). As development proceeded, the GFP signal was gradually constrained to the pharyngeal region and cartilage tissue (H, I, J, K and L). From 96 hpf, apparent signal could be observed in the gastrointestinal organs (K) and serotonergic neuroepithelial cells on the skin (L). B and C, lateral view with animal pole to the top. D and E, lateral view with anterior to the top. F-I and K, lateral views with head to left. J and L, ventral views with anterior to the top.
Reprinted from Developmental Biology, 421(1), Hou, N., Yang, Y., Scott, I.C., Lou, X., The Sec domain protein Scfd1 facilitates trafficking of ECM components during chondrogenesis, 8-15, Copyright (2017) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Biol.