Fig. 3
- ID
- ZDB-IMAGE-170123-11
- Genes
- Antibodies
- Source
- Figures for Miranda-Rodríguez et al., 2017
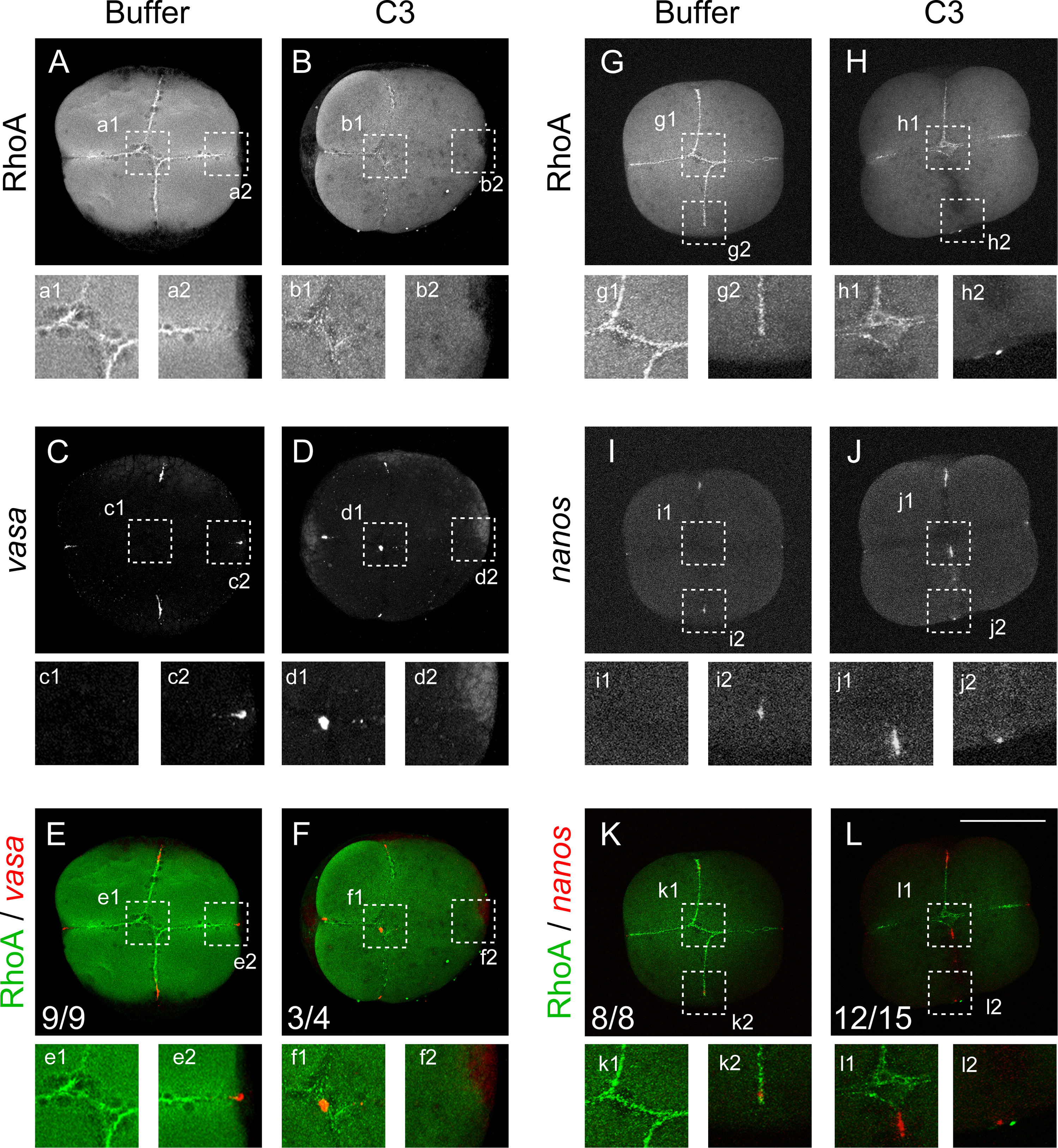
Fig. 3
RhoA inhibition interferes with animal germ plasm localization. RhoA immunolocalization (A, B, G and H) vasa mRNA localization (C, and D), nanos mRNA localization (I and J) by fluorescent whole mount in situ hybridization. Embryos injected with buffer (A, C and E; n=9) and (G, I and K; n=8) or with the RhoA inhibitor C3 (B, D and F; n=4) and (H, J and L; n=15). (E and F; K and L) images superimpositions of double labeled embryos with RhoA immunolocalization (green) and vasa or nanos fluorescent in situ hybridization (red) respectively. Insets show image magnification of the corresponding first two-cleavage furrow intersection (e1, f1, k1 and l1) or cleavage furrow edge (e2, f2, k2 and l2). Scale bar 250 μm.
Reprinted from Developmental Biology, 421(1), Miranda-Rodríguez, J.R., Salas-Vidal, E., Lomelí, H., Zurita, M., Schnabel, D., RhoA/ROCK pathway activity is essential for the correct localization of the germ plasm mRNAs in zebrafish embryos, 27-42, Copyright (2017) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Biol.