Fig. 3
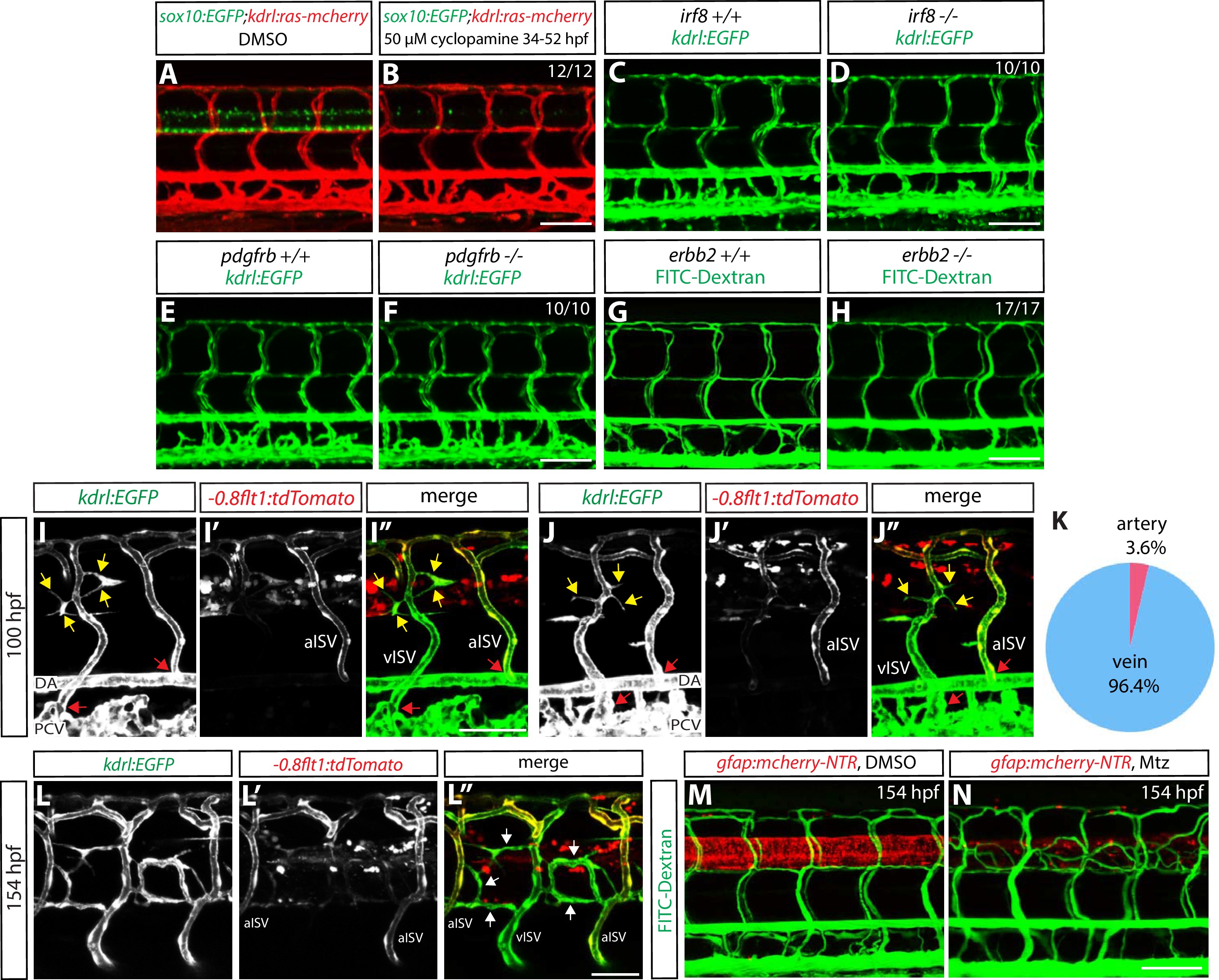
Genetic ablation of CNS radial glia leads to selective over-sprouting of venous ISVs, and ablation of other CNS or PNS cell types does not cause this phenotype.
(A and B) 154 hpf Tg(sox10:EGFP);Tg(kdrl:ras-mcherry) trunks after treatment with DMSO (A) or 50 µM cyclopamine (B) between 34 and 52 hpf. The ectopic ISV sprouting phenotype observed after radial glia ablation is not found in fish treated with cyclopamine, which show a dramatically reduced number of spinal cord oligodendrocytes and oligodendrocyte precursor cells. Scale bar, 100 µm. (C and D) 154 hpf Tg(kdrl:EGFP) irf8+/+ (C) and irf8-/- (D) trunk vasculature. The ectopic ISV sprouting phenotype observed after radial glia ablation is not seen in irf8-/- fish. Scale bar, 100 µm. (E and F) 154 hpf Tg(kdrl:EGFP) pdgfrb+/+ (E) and pdgfrb-/- (F) trunk vasculature. The ectopic ISV sprouting phenotype observed after radial glia ablation is not seen in pdgfrb-/- fish. Scale bar, 100 µm. (G and H) 154 hpf erbb2+/+ (G) and erbb2-/- (H) trunk vasculature visualized by FITC-dextran microangiography. The ectopic ISV sprouting phenotype observed after radial glia ablation is not seen in erbb2-/- fish. Scale bar, 100 µm. (I–I” and J–J”) 100 hpf TgBAC(gfap:gal4ff);Tg(UAS:mcherry-NTR);Tg(kdrl:EGFP);Tg(-0.8flt1:tdTomato) fish that were treated with 2 mM Mtz starting at 30 hpf. Tg(-0.8flt1:tdTomato) expression labels arterial ISVs strongly and venous ISVs weakly (I’ and J’), and ectopic vessel sprouts after radial glia ablation derive from venous ISVs in most cases (yellow arrows). Red arrows point to ISVs’ connection sites with their axial vessels, namely the dorsal aorta (DA) and posterior cardinal vein (PCV), confirming the identity of aISVs and vISVs as revealed by the differential Tg(-0.8flt1:tdTomato) expression in these vessels. Scale bar, 50 µm. (K) Quantification after radial glia ablation of ectopic sprouts that derive from aISVs or vISVs at 100 hpf. A vast majority of the ectopic sprouts derive from vISVs (106 out of 110 ectopic sprouts derived from vISVs in 17 fish). (L–L”) High magnification images of a 154 hpf TgBAC(gfap:gal4ff);Tg(UAS:mcherry-NTR);Tg(kdrl:EGFP);Tg(-0.8flt1:tdTomato) trunk after radial glia ablation. The animal was treated with 2 mM Mtz between 30 and 154 hpf. Ectopic vessels in the dorsal trunk after radial glia ablation exhibit weak Tg(-0.8flt1:tdTomato) expression as vISVs do (white arrows, L”). Scale bar, 50 µm. (M and N) 154 hpf TgBAC(gfap:gal4ff);Tg(UAS:mcherry-NTR) larvae that were injected with FITC-Dextran nanocrystals. Animals were treated with DMSO (M) or 2 mM Mtz (N) between 30 and 154 hpf, and then injected with FITC-Dextran nanocrystals at 154 hpf. FITC-dextran nanocrystals that were injected into the common cardinal vein circulated and labeled the trunk vasculature as shown in the DMSO-treated larva (M). Ectopic blood vessels that emerged after radial glia ablation were labelled by FITC-dextran nanocrystals (N), showing that these ectopic vessels are part of the circulatory loop. Scale bar, 100 µm.