Fig. 1
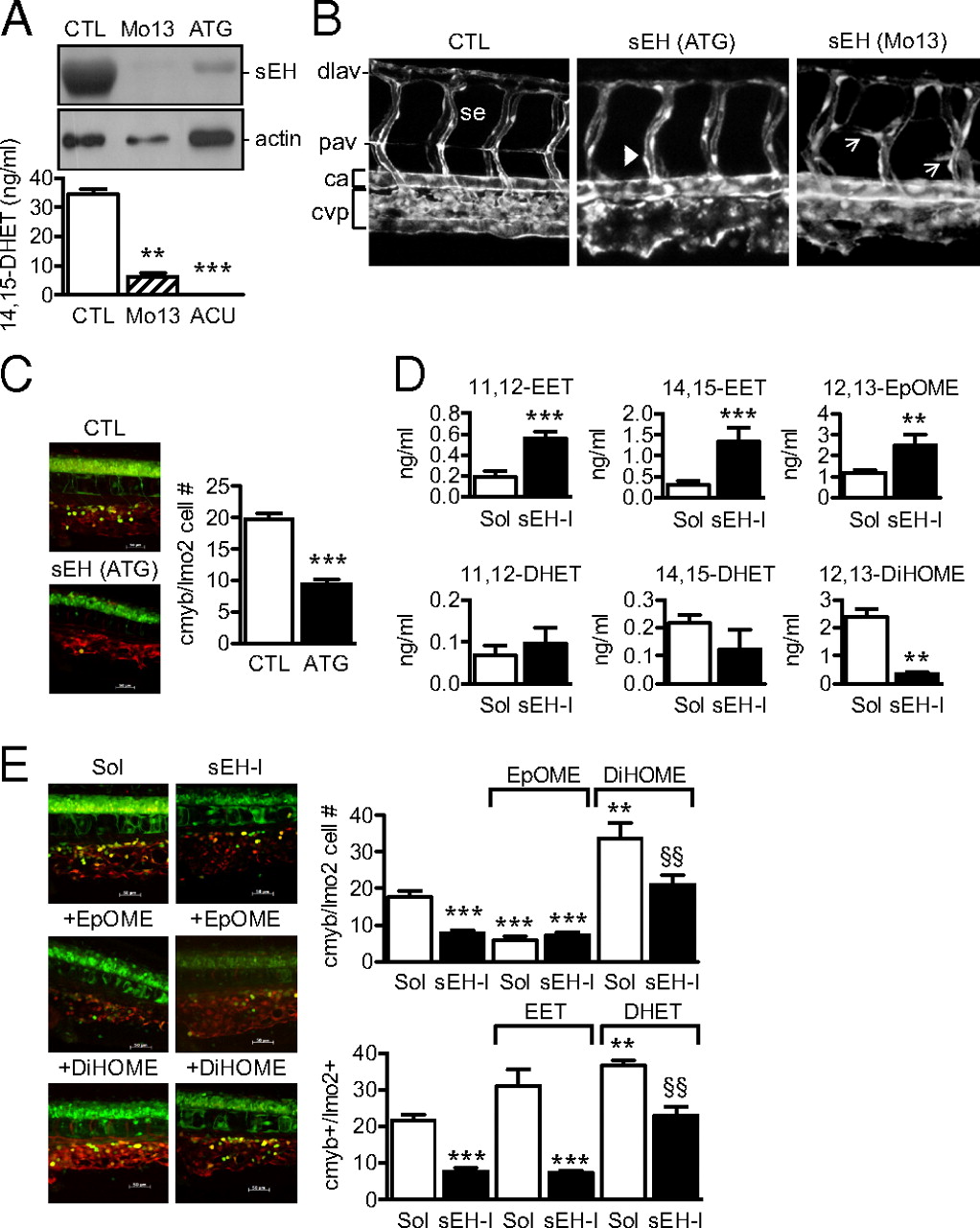
Role of the sEH in the differentiation of the CVP and the caudal hematopoietic tissue in zebrafish. (A) sEH protein expression and activity in 4-d-old zebrafish embryos treated with control (CTL), sEH-ATG or sEH-Mo13 morpholinos. (B) Confocal images of the CVP in Tg(kdrl:EGFP) zebrafish (48 hpf) treated with control or sEH morpholinos. The anterior part of the embryos is on the left; ca, caudal artery; dlav, dorsal longitudinal anastomotic vessel; se, intersegmental vessel; pav, parachordal vessel. Arrows indicate the delayed secondary sprouting of the parachordal vessels, whereas arrowheads mark missing vessels. (C) Effect of control versus sEH (ATG) morpholinos on the number of cmyb+GFP/lmo2+dsRED cells in the CVP in a 40× field z-stack projection located posterior of the yolk sac extension. (D) 11,12-, 14,15-EET/DHET and 12,13-EpOME/DiHOME levels in extracts from 4-d-old zebrafish treated with solvent (Sol) or the sEH inhibitor t-AUCB (sEH-I). (E) Effect of t-ACUB, 12,13-EpOME, or 12,13-DiHOME on the number of cmyb+GFP/lmo2+dsRED cells in the CVP (four-somite stage until 36 hpf). The graphs summarize data obtained with 5–17 zebrafish per group; **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001 vs. Sol or CTL, §§P < 0.01 vs. sEH-I alone. (Magnification: B, 100×; E, 400×.)