Fig. 4
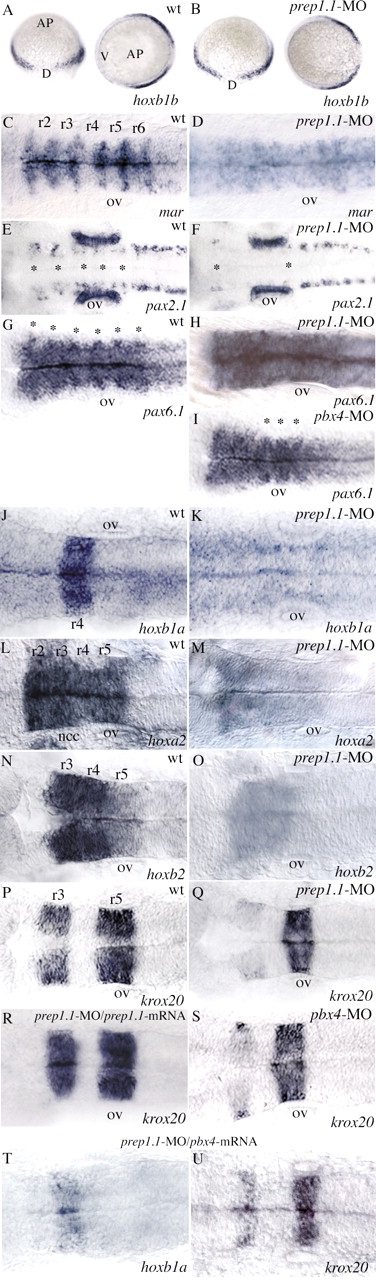
RNA in situ hybridization reveals disruption of hindbrain segmentation and patterning in prep1.1 morphants. (A,B) The pattern of hoxb1b expression is the same as wild type (wt) in prep1.1-MO-treated embryos. AP indicates the animal pole, V and D indicate the ventral and dorsal side of the embryo respectively. (C,D) In prep1.1 morphants, mariposa expression is abolished in the six rhombomere boundaries (from r1-r2 to r6-r7). (E,F) prep1.1 morphants lack the two rows of pax2.1-expressing commissural interneurons in the r2-r6 region of the hindbrain (indicated by asterisks). (G-I) The six rhombomere boundaries revealed by pax6.1 expression (from r1-r2 to r6-r7, indicated by asterisks in the wild-type embryo) are completely lost in prep1.1 morphants and only the r4-r5, r5-r6 and r6-r7 boundaries (asterisks) are clearly identifiable in pbx4 morphants. (J,K) hoxb1a expression in r4 is lost in prep1.1 morphants. (L-O) The levels of expression of hoxa2 (r2-r5) and hoxb2 (r3-r5) are severely reduced in prep1.1 morphants. (P-S) In prep1.1 morphants, krox20 expression is reduced only in r3; injection of prep1.1-MOb with a prep1.1 mRNA construct that lacks the sequence complementary to prep1.1-MOb rescues the wild-type phenotype. In pbx4 morphants, krox20 expression in r3 is also very weak. (T,U) Co-injection of pbx4/lzr mRNA in prep1.1 morphants partially rescues hoxb1a levels but does not rescue krox20 in r3. Embryos are stained at 60% epiboly (A,B), 20 hpf (J,K), 24 hpf (C-I,L-S). All embryos, except A and B, are in dorsal views with anterior to the left. Abbreviations: ov, otic vesicle; ncc, neural crest cells. The animals represented in this figure are different from those of Table 1. Quantitative data: (picture) probe, defective/total; (B) hoxb1b, 2/21; (D) mariposa, 21/26; (F) pax2.1, 25/30; (H) pax6.1, 16/18; (K) hoxb1a, 18/21; (M) hoxa2, 17/22; (O) hoxb2, 19/27; (Q) krox20, 19/25; (R) krox20, 7/20 (rescue P<0.01); (S) krox20, 19/23; (T) hoxb1a, 5/11 (rescue P<0.05); (U) krox20, 11/18.