Fig. 1
Genetic Screen Identifies Mutations Affecting Acoustic Startle Habituation
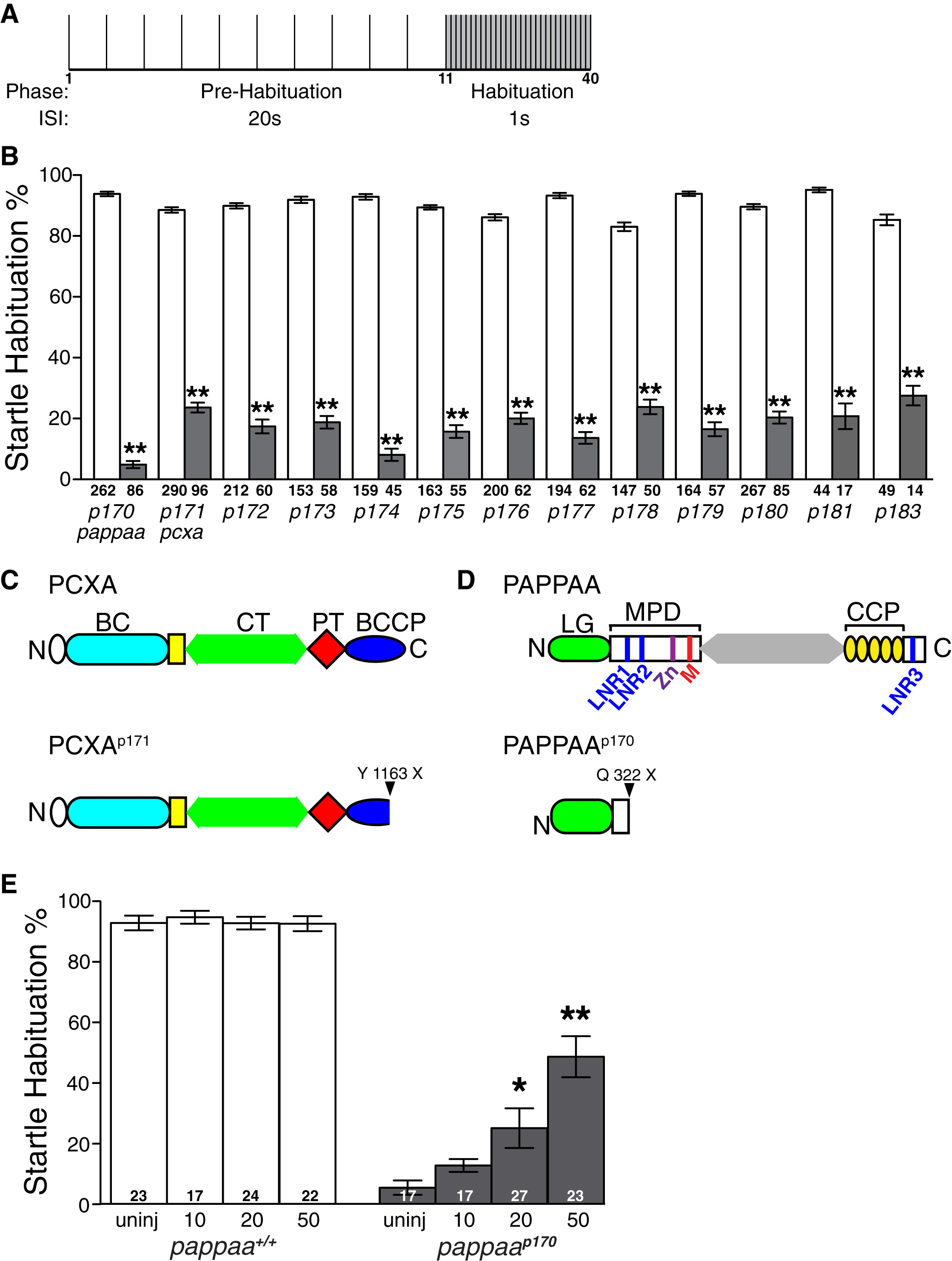
(A) Schematic of acoustic startle habituation assay. Larvae are exposed to 10 non-habituating acoustic stimuli, delivered at 20 s interstimulus intervals (ISI), and then 30 habituating stimuli at a 1 s ISI.
(B) Mean acoustic startle habituation percentage calculated by comparing the average frequency of startle responsiveness of an individual to stimuli 1-10 and stimuli 31-40 (Wolman et al., 2011). Behaviorally defined wild-type siblings shown in white bars, mutants in gray bars.
(C) Estimated truncated PCXAp171 protein in information overloadp171 mutants due to Y1163X mutation. BC, biotin carboxylase; CT, carboxyl transferase; PT, pyruvate carboxylase tetramerization; BCCP, biotin-carboxy carrier protein.
(D) Estimated truncated PAPP-AAp170 protein product in unfilteredp170 mutants due to Q322X mutation. LG, laminin G-like module; LNR, Lin-12/Notch repeats, MPD, metzincin proteolytic domain containing zinc-binding consensus sequence (Zn) and Met-turn motif (M); CCP, complement control protein modules 1-5.
E) pappaap170 larvae injected with increasing doses of wild-type pappaa mRNA show improved habituation at 5 dpf. *p < 0.01, **p < 0.001, ANOVA with Bonferonni correction versus wild-type sibling (B) or uninjected pappaap170 (E) larvae. N = number of larvae shown within or below each bar. Error bars indicate SEM.