Fig. 1
In the spinal cord, pkd2l1+CSF-cNs project an apical extension consisting of one kinocilium and a brush of microvilli into the central canal.
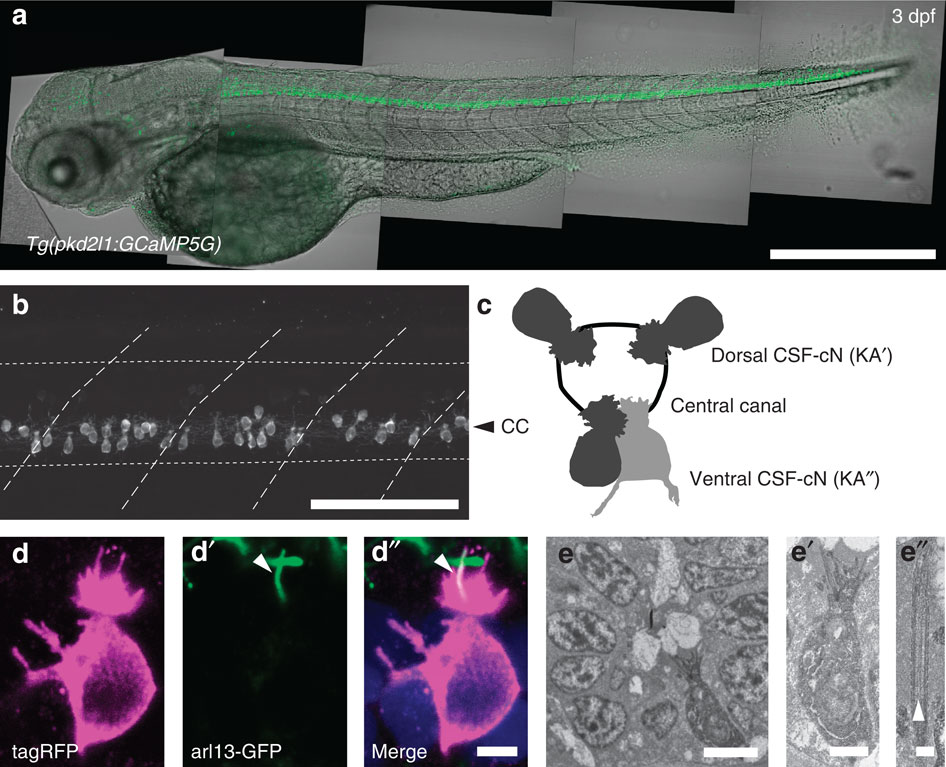
(a) Transmitted and fluorescent image showing that the pkd2l1 promoter in Tg(pkd2l1:GCaMP5G) transgenic larva drives GCaMP5G expression in CSF-cNs along the entire spinal cord. Scale bar: 500 µm. (b) A close up from a lateral view in the same transgenic animal shows the morphology of CSF-cNs as elongated cells with an apical extension reaching the central canal. Scale bar: 100 µm. (c) Schematic depicting dorsal and ventral CSF-cN location around the central canal. (d) Confocal microscopy of 50 µm sections of the 4 dpf triple transgenic larva Tg(pkd2l1:gal4, UAS:tagRFP-CAAX;cmcl2:GFP, βact:Arl13-GFP) shows that CSF-cNs project one Arl13-GFP+ cilium (arrowhead) and multiple microvilli into the CSF. Scale bar: 3 µm. (e) Transmission electron microscopy in Tg(pkd2l1:Gal4) larvae injected with UAS:APEX2-tagRFP shows a single ventral CSF-cN reaching the central canal (close up in (e′), scale bar: 2µm) and exhibiting a motile 9+2 cilium (arrowhead, (e′′), scale bar: 250 nm).