Fig. 3
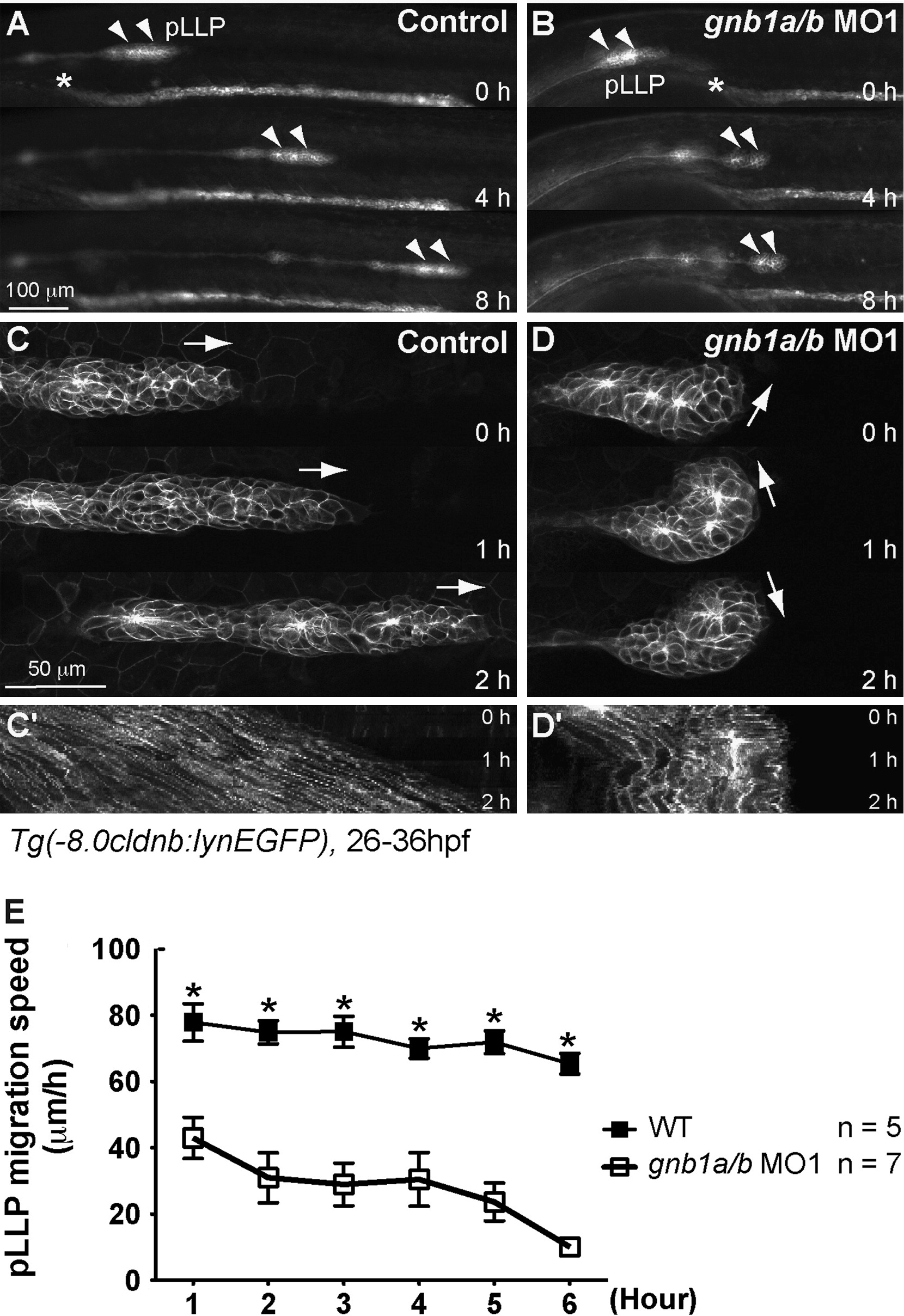
Gβ1 signaling is required for the coordinated movement of cells within the pLLP. (A, B) Snapshots from 8-h epifluorescence time-lapse movies of control (A) or gnb1a/b MO1-injected (B). Tg(-8.0cldnb:lynEGFP) embryos, at 28-36 hpf, using a 5×/NA 0.15 objective (Movies 1 and 2). Lateral views with anterior to the left. Arrowheads, pLLP; *, the anterior-most region of the pronephric duct. (C, D) Snapshots from 2-h confocal time-lapse movies of control (C) or gnb1a/b MO1-injected (D). Tg(-8.0cldnb:lynEGFP) embryos, starting at 30 hpf, using a 20× NA 0.8 objective (Movies 3 and 4). The white arrows in C and D indicate the direction of pLLP migration. (C′-D′) Kymograph analysis showing the cell traces from the 2-h movies in C and D. (E) Speed of migration (in micrometers per hour) of the pLLP in control or gnb1a/b MO1-injected embryos recorded for 6 h from 28 to 34 hpf.
Reprinted from Developmental Biology, 385(2), Xu, H., Ye, D., Behra, M., Burgess, S., Chen, S., and Lin, F., Gbeta1 controls collective cell migration by regulating the protrusive activity of leader cells in the posterior lateral line primordium, 316-27, Copyright (2014) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Biol.