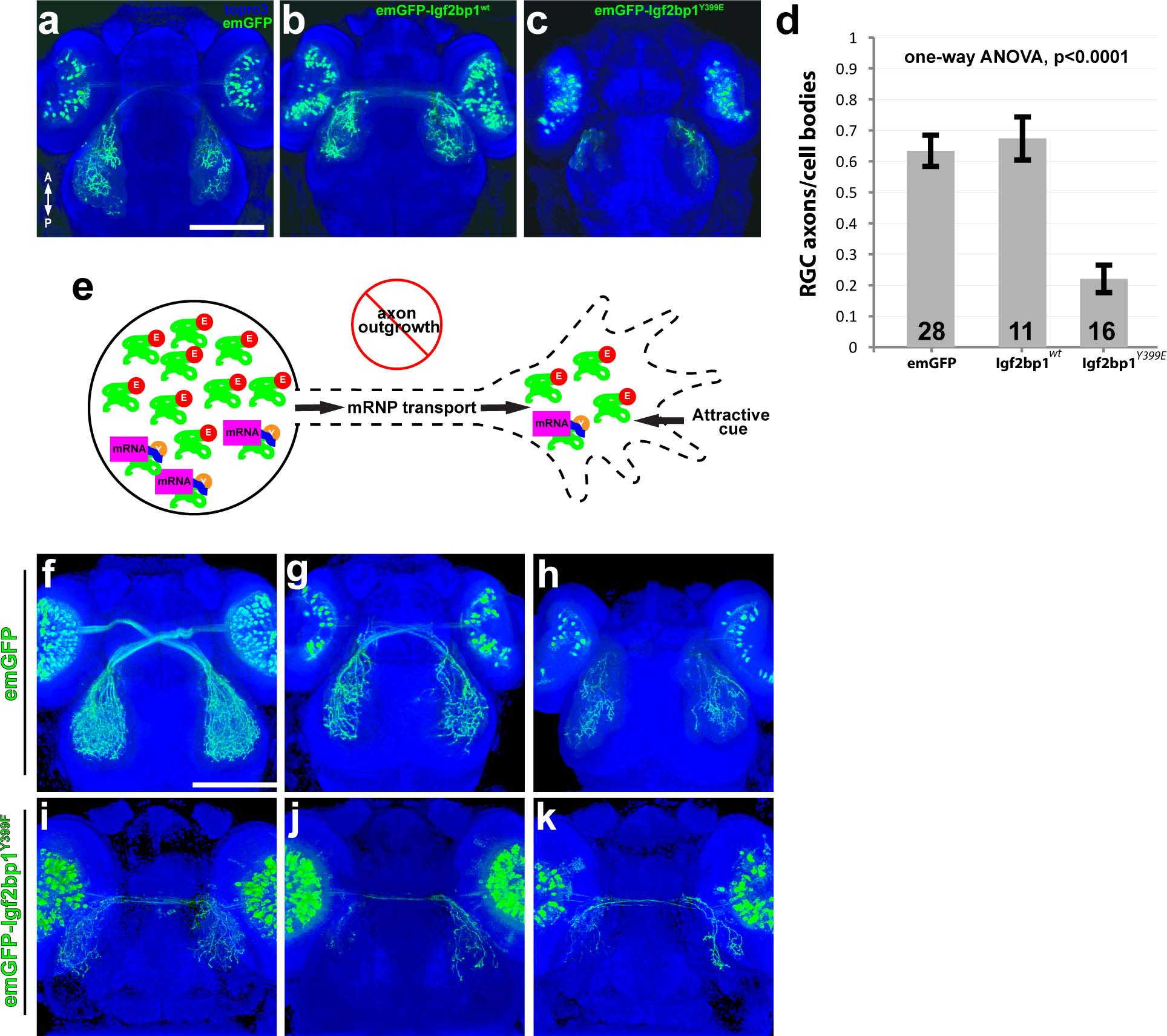
Fig. 5
Expression of emGFP-lgf2bp1Y399E in RGCs disrupts axon outgrowth in vivo.
(a-c) Dorsal confocal projections (30x silicone immersion lens) of Tg(isl2b:emGFP) (a), Tg(isl2b:emGFP-Igf2bp1)wt (b), and Tg(isl2b:emGFP-Igf2bp1)Y399E (c) 3 dpf transient transgenic embryos. (d) Quantification of the ratio of emGFP (green) positive RGCs in the retina to emGFP positive axons on the contralateral tectum per tectum-eye pair (average +/- SEM). A one-way ANOVA (p<0.0001) with a Tukey HSD test (p<0.01) showed that the ratios were significantly different in emGFP-Igf2bp1Y399E (N = 16 tectum-eye pairs, 9 animals) compared to Igf2bp1wt (N = 11 tectum-eye pairs in 7 animals) and emGFP (N = 26 tectum-eye pairs, 16 animals) controls, and controls were not significantly different. (e) Schematic of the predicted mechanism for Igf2bp1Y399E expression preventing axon outgrowth by interfering with endogenous Igf2bp1 by competing for mRNA transport to the growth cone without β-actin mRNA cargo, therefore decreasing the amount of β-actin mRNA available for local translation in the growth cone in response to attractive guidance cues. (f-k) Dorsal confocal projections of Tg(isl2b:emGFP (f-h) and Tg(isl2b:emGFP-Igf2bp1Y399F) (i-k) 3 dpf embryos. Scale bars are 100 µm.