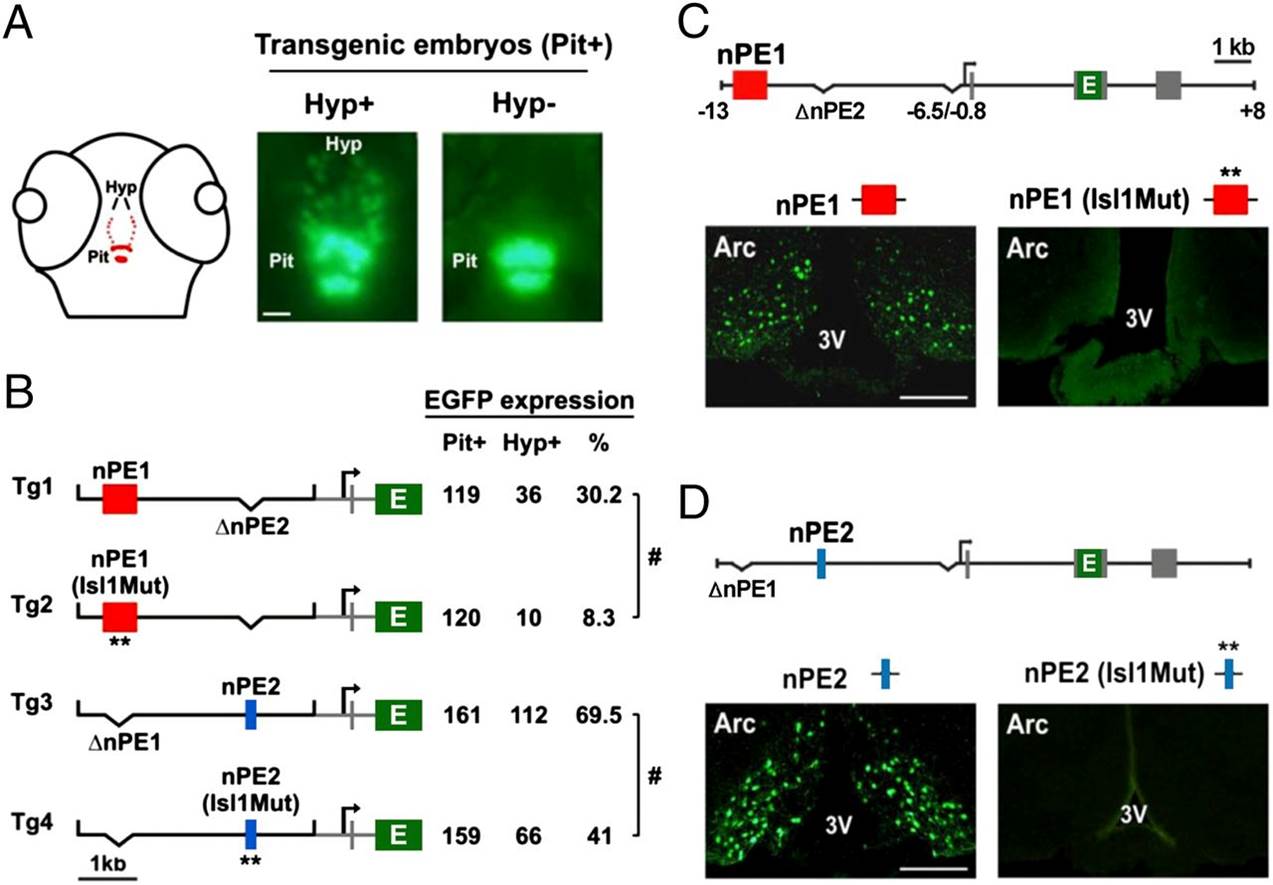
Fig. 3
ISL1 binding sites in nPE1 and nPE2 are important for enhancer function. (A) Schematic of a 72-hpf zebrafish head showing the distribution of pomca-expressing cells (red dots) in the pituitary (Pit) and hypothalamus (Hyp). For transient reporter gene expression analyses, transgenic embryos showing strong pituitary EGFP expression (Pit+) at 72 hpf are selected and then sorted as expressing (Hyp+) or not expressing (Hyp) EGFP in the hypothalamus. (Scale bar, 50 µm.) (B) Expression analyses of transgenes driving EGFP under the control of zebrafish proximal pomca sequences (from 0.6 to +0.4 kb, in gray) and a neuronal mouse Pomc distal module carrying either wild-type or Isl1Mut enhancers nPE1 (red box) or nPE2 (blue box) in transgenic zebrafish. Seventy-two hours postfertilization, transgenic embryos were selected based on pituitary EGFP expression (Pit+), and the number of Pit+ embryos also showing EGFP+ neurons in the hypothalamus (Hyp+) was quantified. #P < 0.0001, Χ2 test. (C) Expression analysis of transgenic mice carrying nPE1 or nPE1 (Isl1Mut) sequences driving EGFP on coronal sections at the hypothalamic arcuate (Arc) level. (D) Expression analysis of transgenic mice carrying nPE2 or nPE2 (Isl1Mut) sequences driving EGFP on coronal sections at the hypothalamic arcuate (Arc) level. 3V, third ventricle. (Scale bar, 500 µm.)