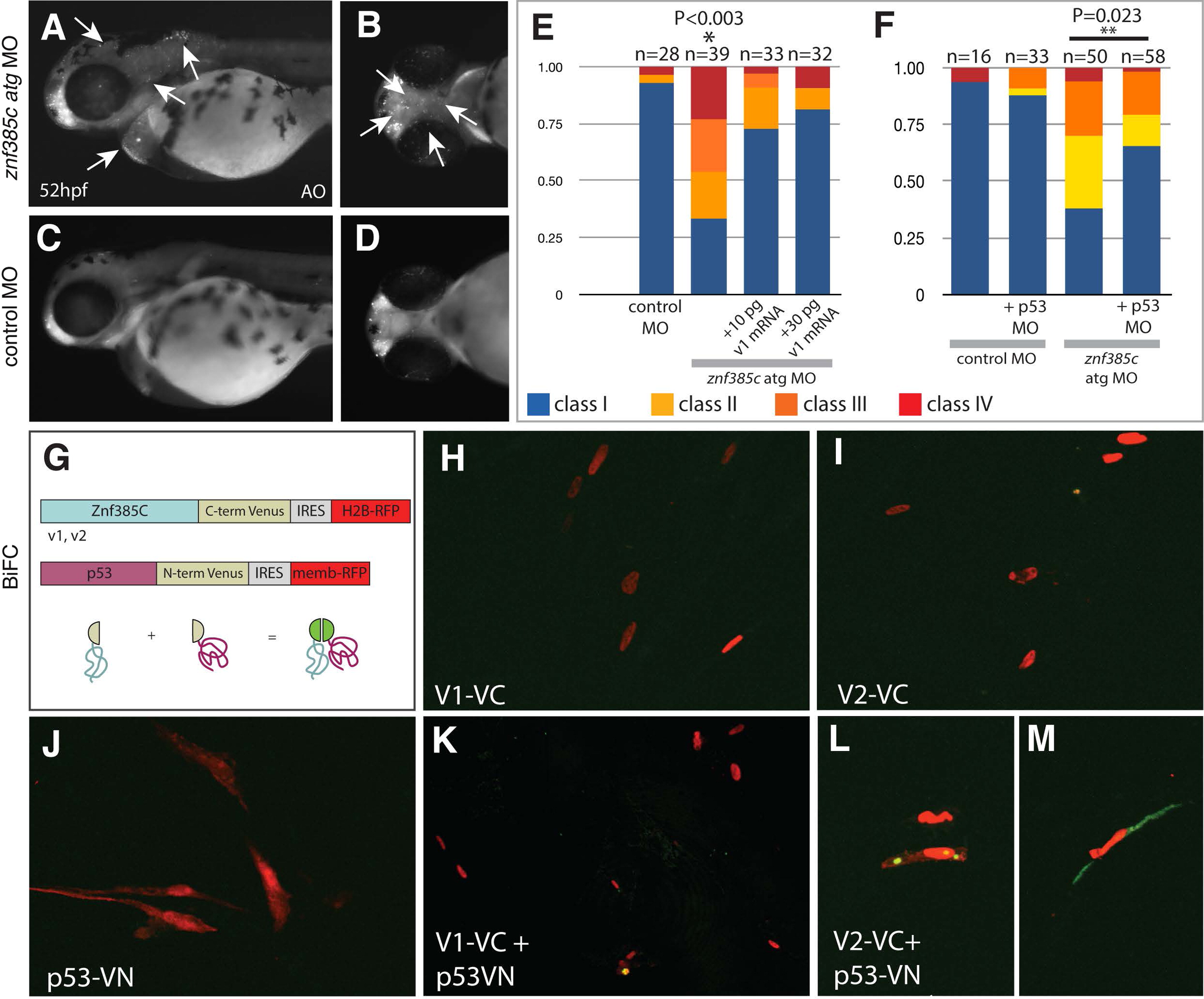
Fig. 3
Znf385C splice variant V2 associates with p53 in the nucleoli and cytoplasm. (A–D) Detection of cell death by Acridine Orange in live znf385c morphant (A and B) and control embryos (C and D) at 52 hpf. Lateral (A and C) and ventral (B and D) views. White arrows point areas of increased cell death in forebrain and hindbrain (A), as well as in heart and pharyngeal region (B). (E and F) Percentage of embryos according to the classes of jaw phenotypes after inactivation of znf385c in zebrafish. Note significant rescue of phenotype by co-injection of full-length mRNA (v1) (E) or partial rescue by co-injection with p53 MO (F). Asterisks indicate statistical significance, NP<0.003 and NNP=0.023. (G) Schematic diagram of BiFC constructs. Sequences encoding Znf385C (v1 or v2) and p53 as a fusion protein to C-terminal (VC) and N-terminal (VN) portions of Venus, respectively. Transfection efficiency was monitored by expression of nuclear H2B-RFP and membrane-RFP, respectively. Green fluorescent signal reveals interaction between Znf385C and p53 fused to hemi-portions of Venus. (H–M) Chicken fibroblast cells transfected with constructs encoding V1–VC (H) or V2–VC (I), and p53-VN (J), alone or combined (K and L). White arrows indicate focal expression of Venus (green) in the nucleoli (L) and in the cytoplasm (M) where V2–VC and p53-VN interact.
Reprinted from Developmental Biology, 400(1), Hochgreb-Hägele, T., Koo, D.E., Bronner, M.E., Znf385C mediates a novel p53-dependent transcriptional switch to control timing of facial bone formation, 23-32, Copyright (2015) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Biol.