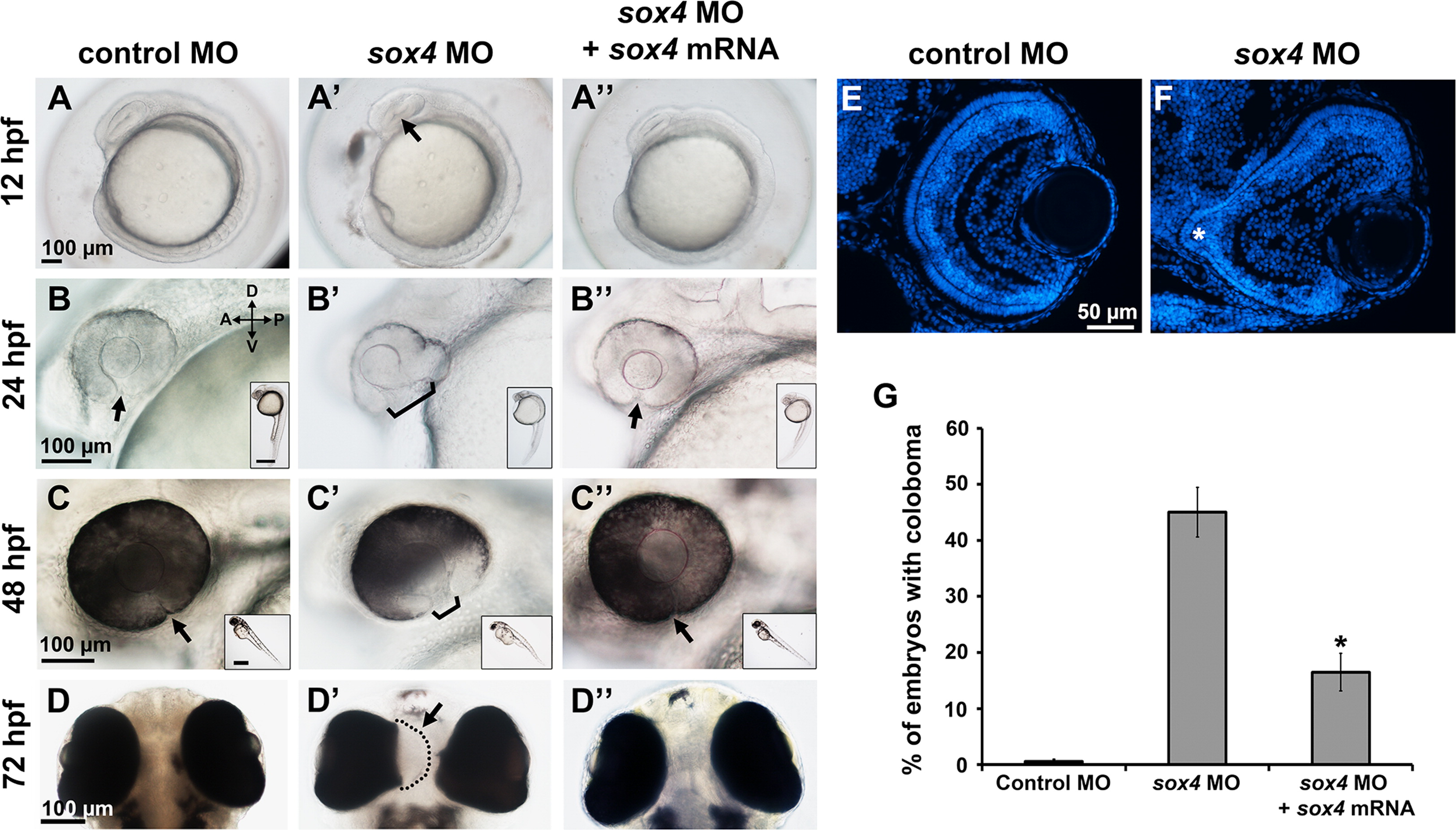
Fig. 2
Knockdown of sox4 causes coloboma. Representative images of control MO-injected embryos (A–D), sox4 MO-injected embryos (A2–D2), and embryos injected with both sox4 MO and sox4 mRNA (A′′–D′′). A minimum of 5 embryos were imaged for each group. Images in A–C′′ are lateral views; images in D–D′′ were taken from the ventral side of the embryo. Insets show the whole body of the same embryo in the larger panel. Arrow in A′ indicates the horizontal crease; arrows and brackets in B–C′′ indicate the choroid fissure. (E-F) Transverse DAPI-stained sections of control and sox4 morphants at 72 hpf. The coloboma in the sox4 morphant retina is prominent (F, asterisk). (G) Quantification of the coloboma phenotype at 48 hpf. In control morphants, 0.61±0.49% of embryos displayed coloboma (n=2/329). In sox4 morphants, 45.01±4.43% of embryos displayed coloboma (n=257/571). Co-injection of sox4 mRNA significantly reduced the incidence of coloboma to 16.49±3.37% (n=31/188; Fisherós exact test, P<0.0001). Scale bars for the insets in B–C′′ equal 500 µm.
Reprinted from Developmental Biology, 399(1), Wen, W., Pillai-Kastoori, L., Wilson, S.G., Morris, A.C., Sox4 regulates choroid fissure closure by limiting hedgehog signaling during ocular morphogenesis, 139-53, Copyright (2015) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Biol.