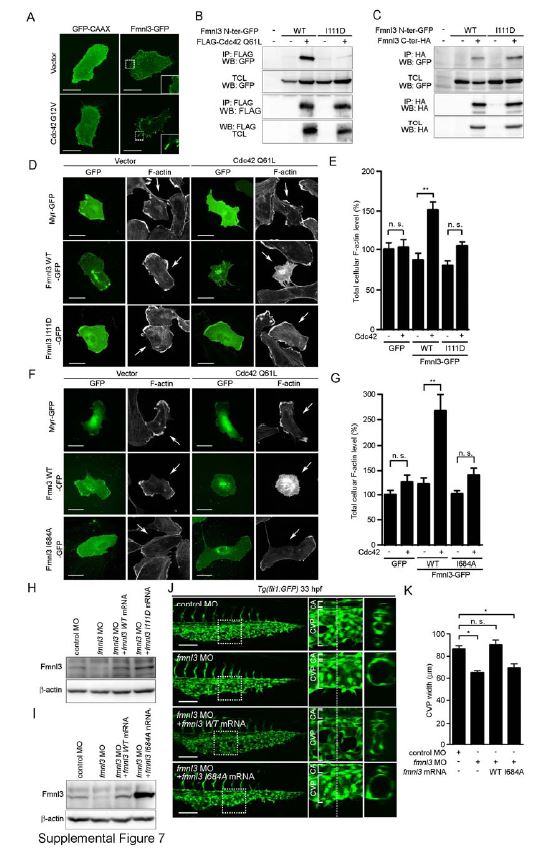
Fig. S7 Cdc42 Activates Fmnl3 to Induce Actin Polymerization. Related to Figure 7. (A) HUVECs were transfected with the plasmid expressing either membrane-targeted GFP (GFP-CAAX, 1 µg) or Fmnl3-GFP (1 µg) together with the empty vector (0.1 µg) or that encoding FLAG-tagged constitutive active form of Cdc42 (Cdc42 G12V, 0.1 µg). The boxed areas are enlarged in the insets. (B) 293T cells were transfected without (-) or with (+) the plasmid encoding either Fmnl3 N-ter-GFP (WT) or Fmnl3 N-ter I111D-GFP (I111D) together with the empty vector or that encoding FLAG-tagged constitutive active form of Cdc42 (FLAG-Cdc42 Q61L) as indicated at the top. Immunoprecipitates (IP: FLAG) of cell lysates and aliquots of total cell lysate (TCL) were subjected to Western blot analyses with anti-GFP and anti-FLAG antibodies as indicated on the left. Note that Fmnl3 N-ter-GFP I111D mutant failed to associate with active form of Cdc42. (C) 293T cells were transfected with the plasmid encoding either Fmnl3 N-ter-GFP (WT) or Fmnl3 N-ter-GFP I111D (I111D) together without (-) or with (+) the vector encoding C-terminally HA-tagged Fmnl3 C-ter mutant (Fmnl3 C-ter-HA) as indicated at the top. Immunoprecipitates (IP: HA) of cell lysates and aliquots of total cell lysate (TCL) were subjected to Western blot analyses with anti-GFP and anti-HA antibodies as indicated on the left. (D) HUVECs transfected with the plasmid encoding Myr-GFP (1 mg), Fmnl3 WT-GFP (1 µg) or its mutant incapable of binding to Cdc42 (Fmnl3 I111D-GFP, 1 µg) together with the empty vector (0.1 µg) or the plasmid expressing Cdc42 Q61L (0.1 µg) were stained with rhodamine-phalloidin (F-actin), as in Figure 6C. Arrows indicate GFP signal-positive cells. (E) Total cellular F-actin levels as observed in D were quantified, as in Figure 6D. Data are expressed as percentages relative to that observed in cells transfected with the empty vector and the Myr-GFP-expressing plasmid, and shown as means ± s.e.m. (n=15). (F) HUVECs transfected with the plasmid encoding either Myr-GFP (1 µg), Fmnl3 WT-GFP (1 µg) or its catalytically inactive mutant (Fmnl3 I684A-GFP, 1 µg) together with the empty vector (0.1 µg) or the plasmid expressing Cdc42 Q61L (0.1 µg) were stained with rhodamine-phalloidin (F-actin), as in Figure 6C. (G) Total cellular F-actin levels as observed in F were quantified, as in Figure 6D. Data are expressed as percentages relative to that observed in the cells transfected with empty vector and Myr-GFP-expressing plasmid, and shown as mean ± s.e.m. (n≥12). (H and I) Lysates from 48 hpf zebrafish embryos injected with 2.5 ng control MO or 2.5 ng fmnl3 MO together without or with either 100 pg MO-resistant fmnl3 WT mRNA, 100 pg MO-resistant fmnl3 I111D mRNA (H) or 100 pg MO-resistant fmnl3 I684A mRNA (I) were subjected to Western blot analysis with anti-Fmnl3 and anti-β-actin antibodies. (J) Projection view of confocal z-stack images of the caudal regions of 33 hpf Tg(fli1:GFP) embryos injected with control MO or fmnl3 MO together with vehicle or MO-resistant mRNA encoding wild type Fmnl3 or Fmnl3 I684A are shown, as in Figure 1G. (K) The width of CVP as observed in J was quantified, as in Figure 1H (n≥5). Scale bars, 30 µm (A, D and F) and 100 µm (J). *p<0.05, **p<0.01. n.s., no significance.
Reprinted from Developmental Cell, 32, Wakayama, Y., Fukuhara, S., Ando, K., Matsuda, M., Mochizuki, N., Cdc42 Mediates Bmp-Induced Sprouting Angiogenesis through Fmnl3-Driven Assembly of Endothelial Filopodia in Zebrafish, 109-22, Copyright (2015) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Cell