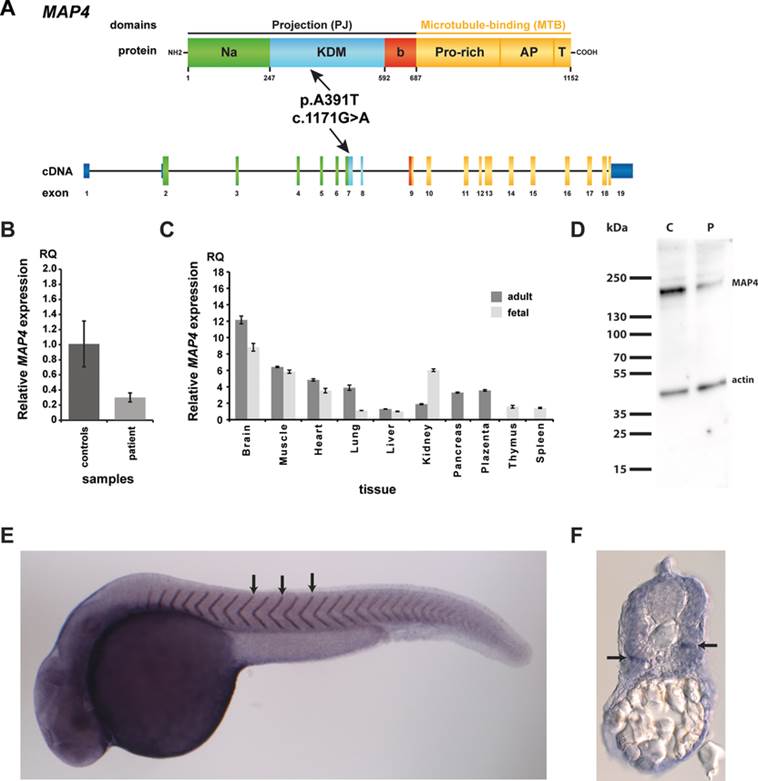
Fig. 3
Expression analyses of MAP4 in patient cells, tissue panels, and zebrafish. A: Schematic drawing of MAP4 at transcriptional and protein level. The 3.459 bp cDNA encodes for a 1,152 amino acid protein of the microtubule-associated protein family. The protein contains two domains, the C-terminal MTB and the N-terminal projection (PJ) domain (Na: N-terminal acidic region; KDM: KDM-repeated sequence region; b, b-region; Pro-rich, proline-rich region; AP, assembly-promoting region; T, tail region) [Iida et al., 2002]. The homozygous variant c.1171G>A (black arrows) found in both patients is located in exon 7 corresponding to the KDM region of the PJ domain. B: In comparison to 10 healthy controls, we observed a significant decrease of the MAP4 expression in patient lymphocytes. C: Expression analysis of different human adult and fetal tissues demonstrated ubiquitous expression of MAP4. D: Western blot analysis of a fibroblast cell line of the patient 2 (P) compared with a healthy control individual (note the reduced protein level of MAP4 in the patient). E–F: Whole mount in situ hybridization in the model organism zebrafish (Danio rerio) showed ubiquitous expression of map4 in the whole embryo. E: Strongest map4 signal was observed in the somite boundaries representing the embryonic body segments (black arrows). F: A transverse section also showed ubiquitous expression of map4 throughout the body trunk, including the somites. Cells dorsal to the horizontal myoseptum (arrow), a connecting tissue dividing the myomeres into two sections, seemed to show a stronger signal than ventral cells.