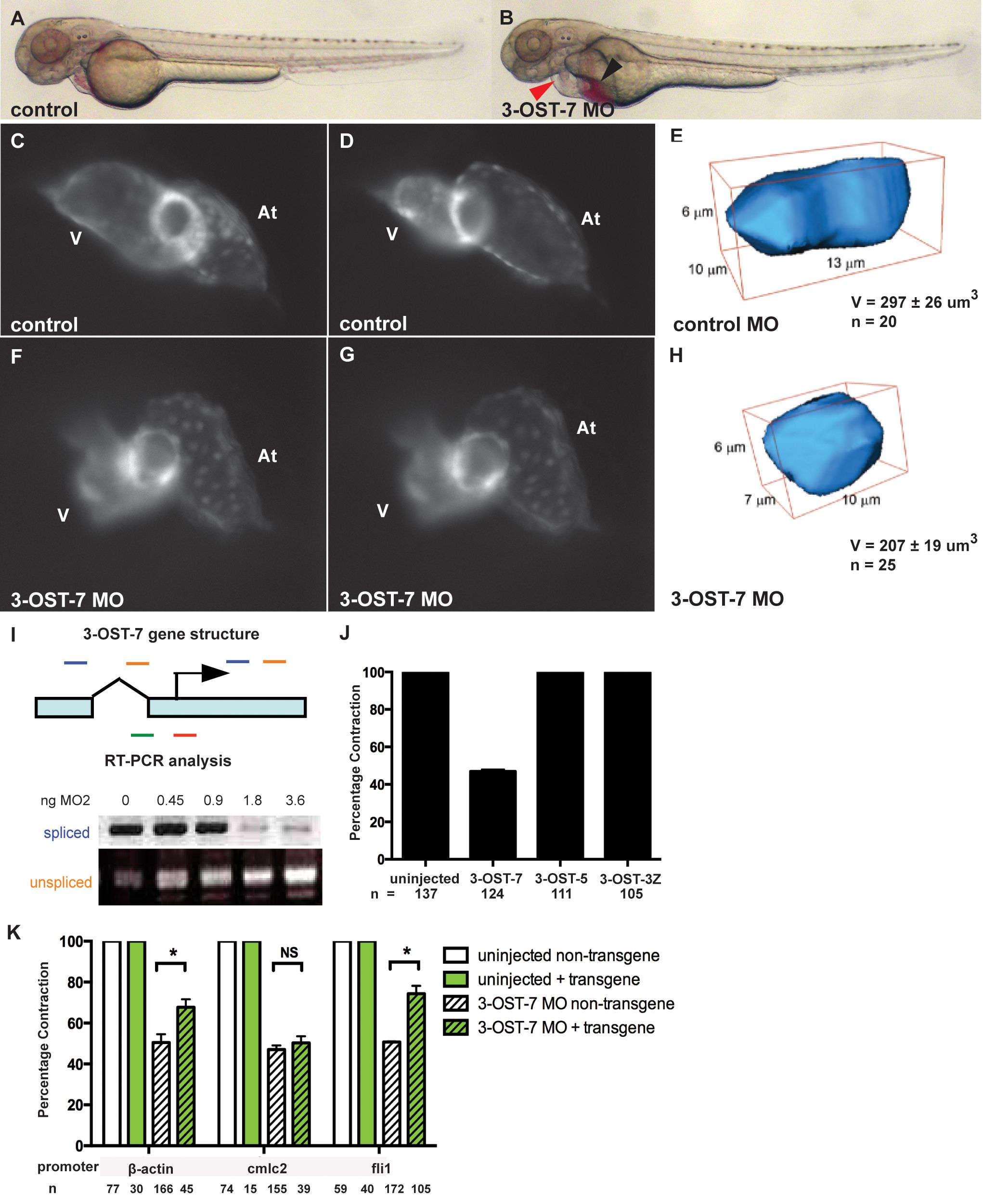
Fig. 1
3-OST-7 is required for ventricular contraction in the zebrafish heart.
Lateral views of control (uninjected, wild-type) (A) and 3-OST-7 morphant (B) embryos at 48 hpf showing edema (red arrowhead) and blood pooling (black arrowhead) with knockdown of 3-OST-7. Lateral views of hearts in control (C–D) and 3-OST-7 morphant (F–G) Tg(cmlc2:gfp) embryos at periods of ventricular diastole (C and F) and systole (D and G). 3D-reconstructed ventricular cell in control (E) and 3-OST-7 morphant (H) embryos show decreased volume (V) in morphants. (I) Gene structure of 3-OST-7 showing MO targets (red for MO1 and green for MO2) and primer sets used for RT-PCR analysis (blue and orange bars). RT-PCR analysis showing decrease in spliced and increase in unspliced products with increasing dose of MO injected. (J) Percentage contraction of embryos in different 3-OST knockdowns (3-OST-7, 3-OST-5, 3-OST-3Z). Only knockdown of 3-OST-7 MO resulted in ventricular noncontraction. (K) Percentage contraction of embryos in rescue experiments using three different transgenes. Uninjected embryos with (green bar) or without (white bar) the transgene had normal ventricular contraction. Injection of 3-OST-7 MO2 in Tg(β-actin:3-OST-7-IEP) and Tg(fli1:3-OST-7-IEP) embryos rescued the noncontracting ventricle phenotype (p = 0.039 and p = 0.0036, respectively, *). Injection of 3-OST-7 MO2 in Tg(cmlc2:3-OST-7-IEP) did not rescue the phenotype (p = 0.44, NS). Graphs depict the percentage of embryos with phenotype in 3-OST-7-overexpressing (GFP+, green hatched) or non-3-OST-7-overexpressing (GFP-, white hatched) embryos from individual crosses between one of three transgenic founders and wild-type AB zebrafish. At, atrium; V, ventricle; error bars, SEM.