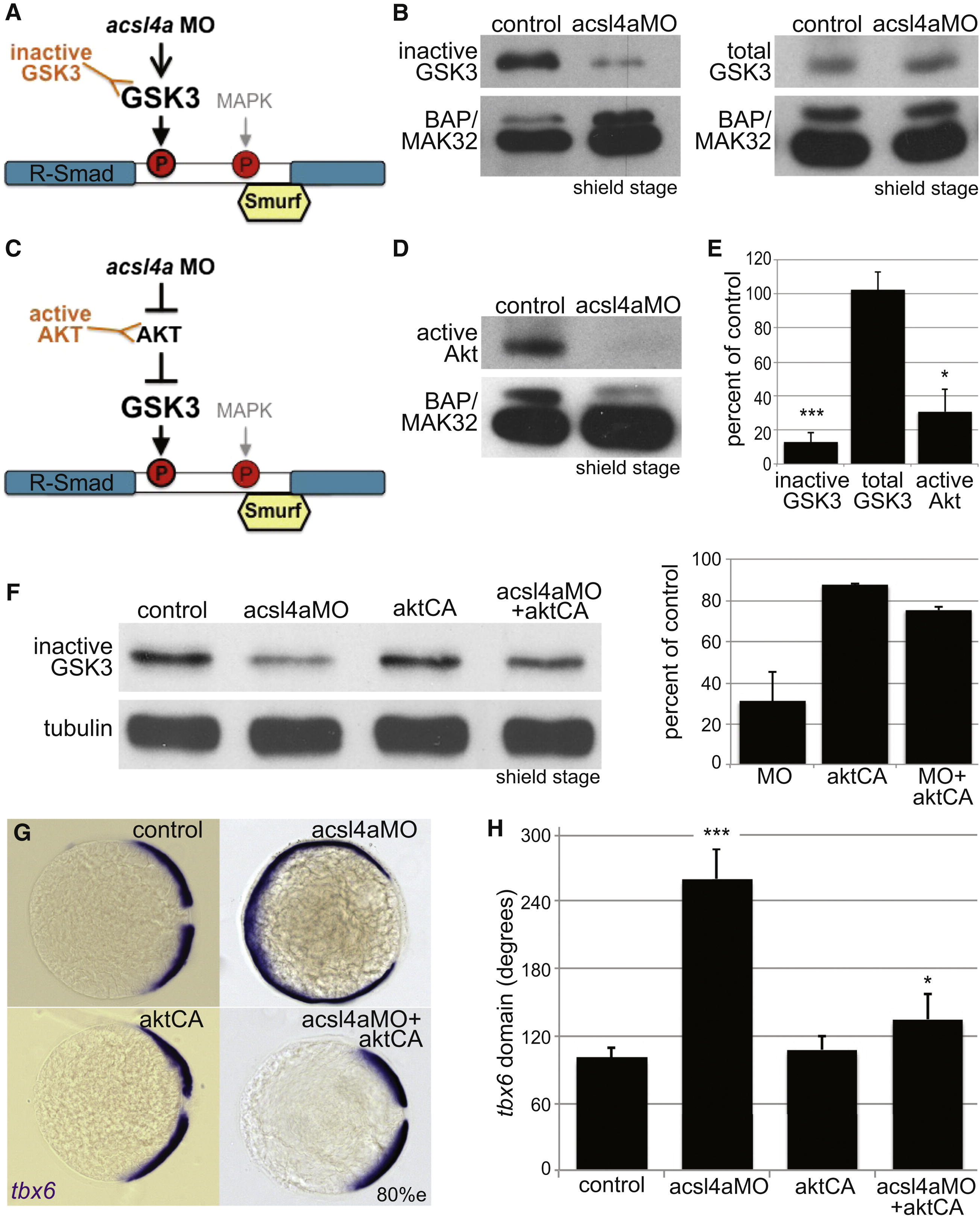
Fig. 6 Acsl4a Regulates GSK3 Activity
(A) An acsl4a MO-dependent increase in GSK3 activity would result in phosphorylation of R-Smad and recruitment of Smurf ubiquitin ligase. There are inhibitory phosphorylation sites (GSK3α Ser21/GSK3β Ser9) that control GSK3 activity level, thus an antibody that recognizes the inhibitory phosphorylation (inactive GSK3) can assay GSK3 activity.
(B) GSK3 activity is increased in acsl4a morphants (500 fmol). (Left) Western blot for inhibitory phosphorylation (GSK3αSer21/GSK3β Ser9) of GSK3 (inactive GSK3). (Right) Western blot for total GSK3β. BAP/MAK32 is the loading control.
(C) GSK3 is inhibited by Akt. An acsl4a MO-dependent decrease in Akt activity would result in decreased inhibition (thus activation) of GSK3. A decrease in Akt activity can be assayed by an antibody specific to active (phosphorylated on Ser473) Akt.
(D) Akt activity is decreased in acsl4a morphants (500 fmol). Western blot for phosphorylated (Ser473) Akt (active AKT). BAP/MAK32 is the loading control.
(E) Quantification of blots from (B) and (D). Data are mean ± SE of three to four experiments and represented as percent of control (p < 0.05 p < 0.001; one sample t test with Bonferroni correction).
(F–H) Constitutively active, myristoylated Akt rescues the acsl4a MO’s dorsalized phenotype. (F) Constitutively active Akt (50–100 pg) decreases GSK3 activity (increase in inactive GSK3) in acsl4a MO-injected (333 fmol) embryos. Data are represented as mean ± SD (n = 2). (G) Expression of tbx6 in a control embryo, embryo injected with acsl4a MO alone (333 fmol), embryo injected with constitutively active akt mRNA (50–100 pg; aktCA), and acsl4a MO with aktCA. Vegetal pole view, dorsal to the right (80% epiboly). (H) Quantification of tbx6 expression domain. Data are represented as mean of experimental means ± pooled SE (n = 3; 20–24 embryos/experiment). ANOVA with Dunnett; p < 0.05, p < 0.0001.
Reprinted from Developmental Cell, 27(6), Miyares, R.L., Stein, C., Renisch, B., Anderson, J.L., Hammerschmidt, M., and Farber, S.A., Long-Chain Acyl-CoA Synthetase 4A Regulates Smad Activity and Dorsoventral Patterning in the Zebrafish Embryo, 635-647, Copyright (2013) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Cell