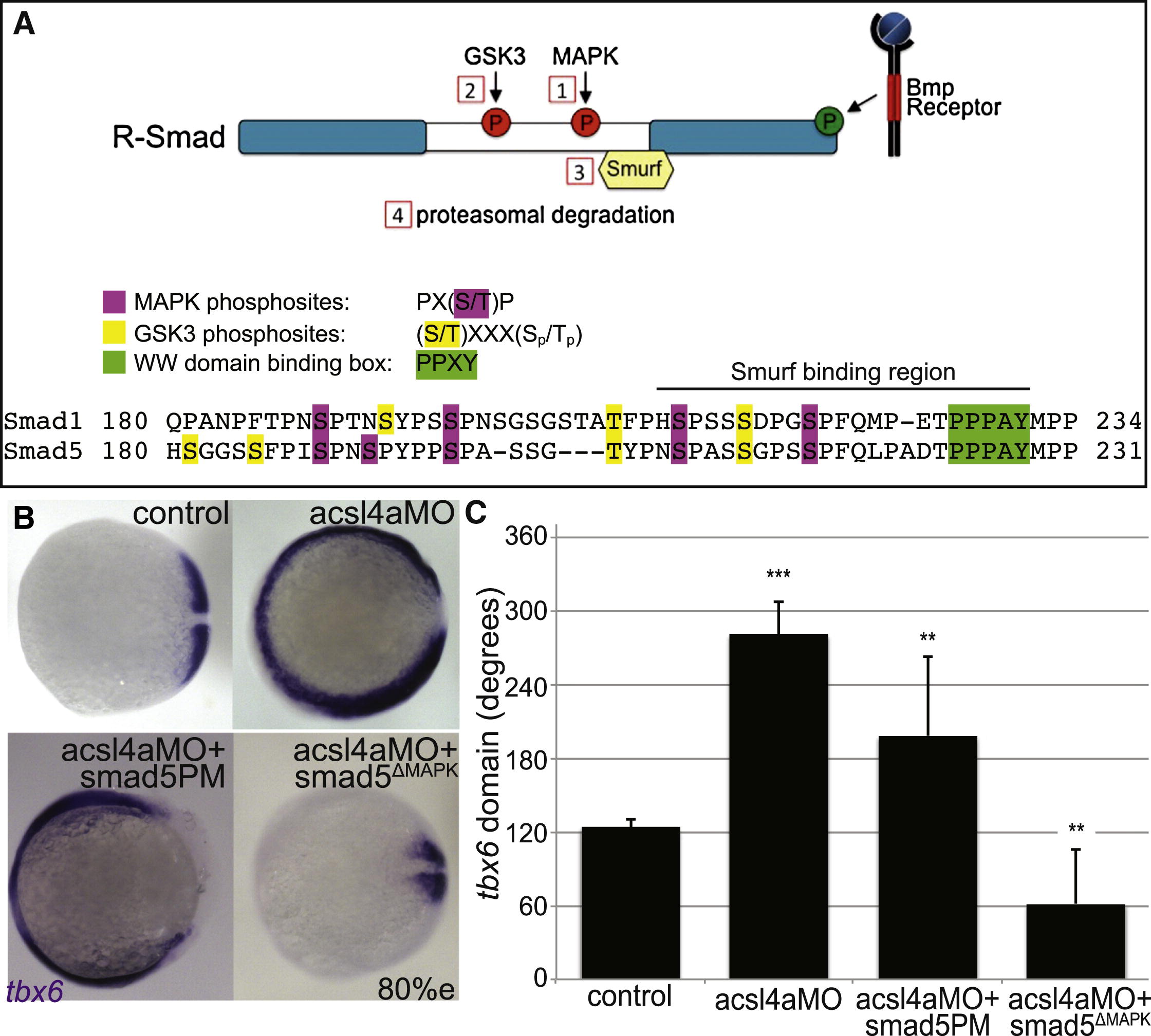
Fig. 4 Acsl4a Acts via R-Smad Phosphorylation at MAPK Consensus Sites
(A) Model of R-Smad regulation by phosphorylation. (Top) The Bmp receptor positively regulates (green) R-Smad activity by phosphorylating the C terminus. Negative regulation (red) of R-Smad occurs in sequential steps: (1) MAPK phosphorylates the R-Smad linker. (2) GSK3 phosphorylates the linker upstream of MAPK phosphoresidues. (3) Smurf1/2 E3 ubiquitin ligase recognizes R-Smad after phosphorylation by MAPK and/or GSK3. (4) Smurf1/2 polyubiquitinates R-Smad, leading to its proteasomal degradation. (Bottom) Sequence alignment of zebrafish Smad1 and Smad5 linker regions with important residues highlighted.
(B) tbx6 expression in a control embryo, embryo injected with acsl4a MO alone (750 fmol), acsl4a MO combined with a C-terminal phosphomimic smad5 mRNA (smad5PM; 1.5 ng), and acsl4a MO combined with a MAPK-insensitive version of smad5 mRNA (smad5ΔMAPK; 1.5 ng). Vegetal pole view, dorsal to the right (80% epiboly).
(C) Quantification of tbx6 expression domain. Data are represented as mean of experimental means ± pooled SE (n = 3–8, 12–80 embryos/experiment). ANOVA with Dunnett post hoc test; p < 0.01, p d 0.005, p < 0.0001; compared to control.
See also Figure S5.
Reprinted from Developmental Cell, 27(6), Miyares, R.L., Stein, C., Renisch, B., Anderson, J.L., Hammerschmidt, M., and Farber, S.A., Long-Chain Acyl-CoA Synthetase 4A Regulates Smad Activity and Dorsoventral Patterning in the Zebrafish Embryo, 635-647, Copyright (2013) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Cell