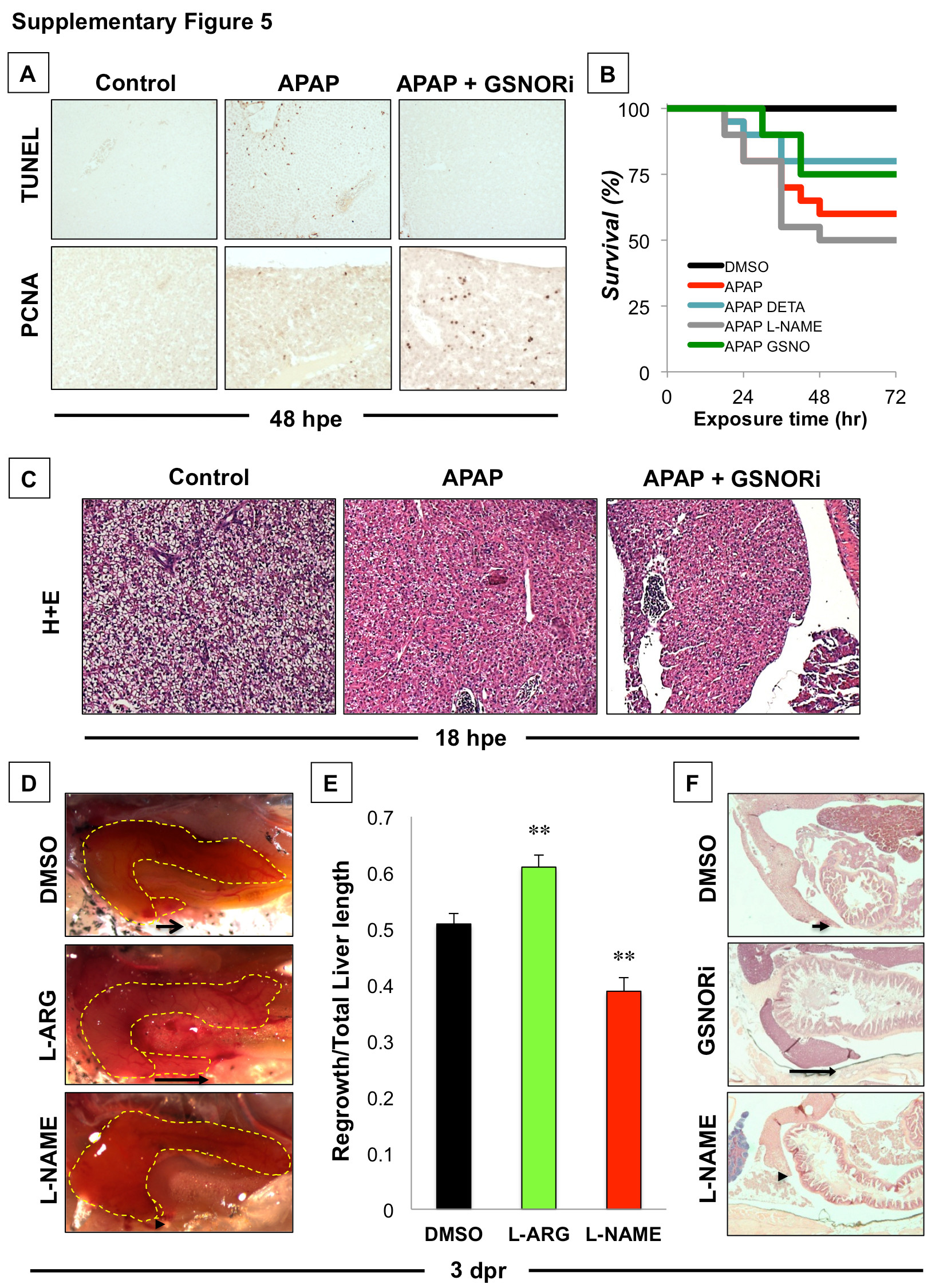
Fig. S5
GSNOR inhibition protects adult zebrafish from APAP-induced toxicity and enhances regeneration following liver injury.
(A) Immunohistochemistry analysis of cell death (TUNEL staining) and proliferation (PCNA staining) in fish exposed to APAP (10 mM) in the presence or absence of GSNORi (1 μM) at 48 hpe. (B) Kaplan-Meier plot of survival in adult fish exposed to APAP (10 mM) for 24 hr in the presence or absence of modulators of NO signaling, including Deta (5 μM), L-NAME (10 μM) and GSNO (5 μM). Chemicals were removed 24 hpe, fish were reintroduced into fresh water and survival was monitored over 72 hr. N = 20 fish / treatment. (C) Hepatic histology (H+E staining) in nrf2 mutant fish (nfe2l2afh318) exposed to APAP (10 mM) in the presence or absence of GSNORi (1 μM) at 18 hpe. (D) Liver regeneration following partial hepatectomy in adult zebrafish exposed to modulators of NO signaling at 3 days post resection (dpr). Adult fish were exposed to DMSO, L-Arg (10 μM) or L-NAME (10 μM) 6 hr after surgery for 24 hr. Representative en bloc dissection photographs were taken at 2.5x magnification. (D) Quantification of liver regeneration as determined by the length of regrowth from the resection margin divided by the total length of the inferior lobe. N=10; ANOVA, **p<0.01. (E) Histological evaluation of liver regeneration following partial hepatectomy at 3 dpr. Fish were sectioned and stained with hematoxylin and eosin (H+E). Representative sections were taken at 2.5x magnification.